Veritabanı Bağlantı Havuzu (Pooling): Performansın Gizli Kahramanı
SQLAlchemy QueuePool, PgBouncer mimarileri ve yüksek trafikli sistemlerde veritabanı bağlantı yönetimi için production-grade stratejiler.
Kariyerimin ilk yıllarında yönettiğim e-ticaret sitesinin bir “Black Friday” gecesinde çökmesini asla unutmam. Kod tarafında her şey optimizeydi, cache mekanizmaları çalışıyordu ama site yanıt vermiyordu. Loglarda gördüğüm tek bir satır, o geceyi uykusuz geçirmemize yetti: FATAL: remaining connection slots are reserved for non-replication superuser connections.
Türkçesi şuydu: PostgreSQL kapıları kapatmıştı. Mesele sorguların yavaş olması değil, veritabanına “Merhaba” diyecek kapı kalmamasıydı. O gün öğrendiğim ders, yazılım mühendisliğinin temel doğrularından biri oldu: Veritabanı bağlantısı, RAM veya CPU’dan daha pahalı bir kaynaktır.
Bugün, sistemlerinizi bu darboğazdan kurtaracak teknikten, Connection Pooling‘den ve üretim ortamındaki kritik ince ayarlardan bahsedeceğiz.
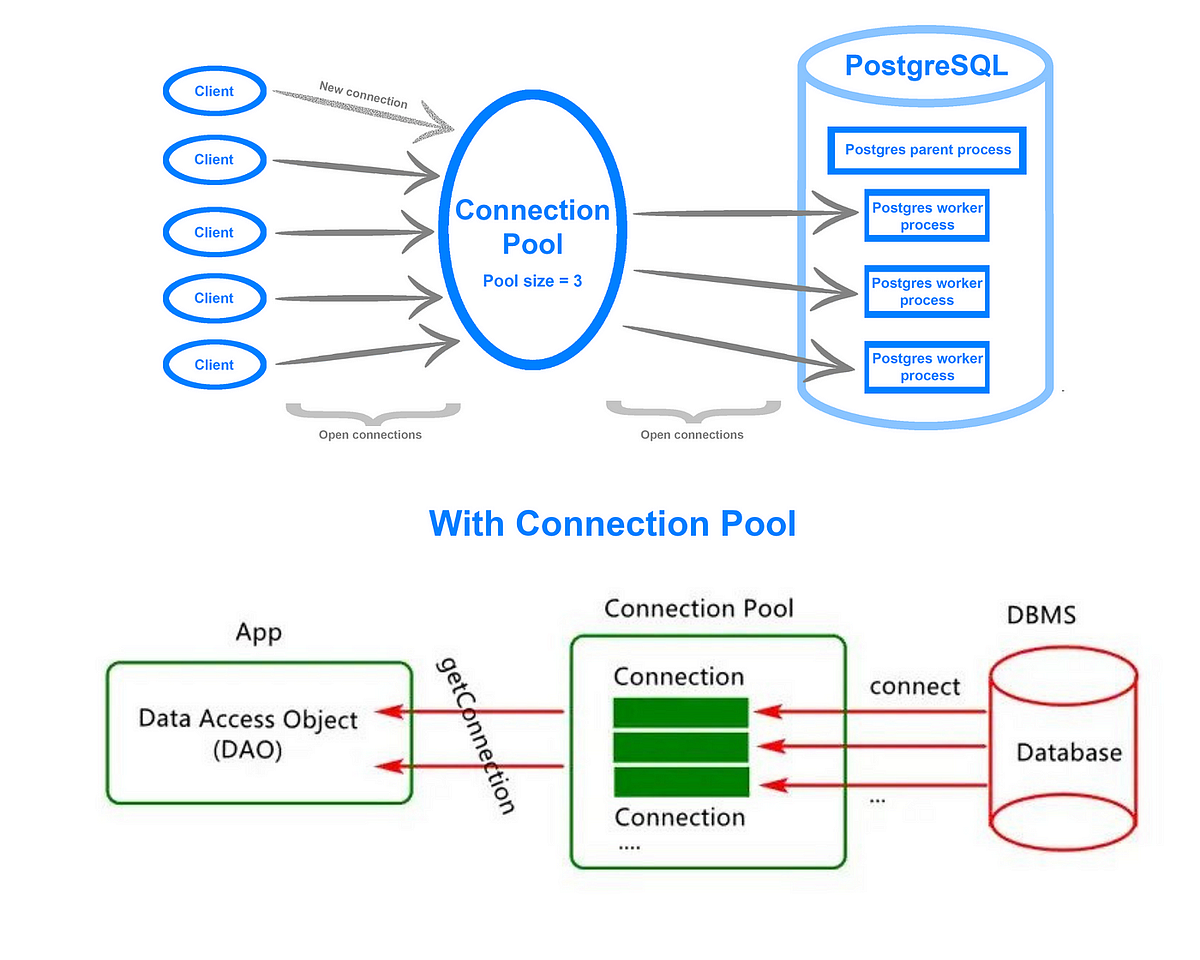 Bağlantı havuzu mimarisi: Uygulama ve veritabanı arasında hayati bir tampon bölge.
Bağlantı havuzu mimarisi: Uygulama ve veritabanı arasında hayati bir tampon bölge.
1. Bağlantı Maliyeti: Neden Bu Kadar Pahalı?
Bir veritabanı bağlantısı açmak (Connection Handshake), basit bir fonksiyon çağrısı değildir. Arka planda şu adımlar gerçekleşir:
- Network I/O: TCP 3-way handshake başlatılır.
- Authentication: Kullanıcı adı/şifre gönderilir, şifrelenir ve doğrulanır.
- Process Forking: PostgreSQL (veya benzeri sistemler) her yeni bağlantı için işletim sistemi seviyesinde yeni bir process
forkeder. Bu, ciddi bir RAM maliyetidir. - Backend Initialization: Session değişkenleri ve bellek alanları ayrılır.
Basit bir SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=1 sorgusu optimize edilmiş bir veritabanında 5ms sürerken, o sorguyu atabilmek için gereken bağlantıyı açmak 100ms - 200ms sürebilir. Eğer her HTTP isteğinde yeni bir bağlantı açıp kapatıyorsanız, uygulamanızın performansının %95’ini çöpe atıyorsunuz demektir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# ANTI-PATTERN: Her istekte bağlantı açma maliyeti
import psycopg2
import time
def get_user_bad_practice(user_id):
start = time.time()
conn = psycopg2.connect("...") # Pahalı işlem (~150ms)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT ...") # Ucuz işlem (~5ms)
conn.close() # Kaynak israfı
end = time.time()
print(f"Total Time: {(end-start)*1000}ms")
2. SQLAlchemy ile Akıllı Havuz Yönetimi
Python ekosisteminde SQLAlchemy kullanıyorsanız QueuePool mekanizması yerleşik olarak gelir. Ancak varsayılan ayarlar (pool_size=5, max_overflow=10) orta ölçekli bir proje için yetersiz kalabilir.
 SQLAlchemy’nin havuz (pool) ve taşma (overflow) mantığının görselleştirilmesi.
SQLAlchemy’nin havuz (pool) ve taşma (overflow) mantığının görselleştirilmesi.
Kritik Konfigürasyonlar
Burada ezbere değer girmemek hayati önem taşır. Matematik basittir: Toplam DB Bağlantısı = (Pod Sayısı) x (Pool Size + Max Overflow)
Eğer PostgreSQL max_connections=100 ise ve siz 20 tane Kubernetes pod’u çalıştırıyorsanız, her pod için pool_size=5 vermek bile limiti doldurur (20x5=100). Overflow devreye girdiği an hatalar başlar.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql://user:pass@host/db",
# Havuzda sürekli aktif tutulacak bağlantı sayısı
pool_size=20,
# Trafik arttığında geçici olarak açılabilecek EK bağlantı sayısı
max_overflow=10,
# Bağlantı kopmuş mu? (Production'da MUTLAKA True olmalı)
pool_pre_ping=True,
# Bağlantıların belirli süre sonra yenilenmesi (Sessiz kopmaları önler)
pool_recycle=3600
)
Senior Notu:
pool_pre_ping=Trueayarı, havuza dönen bağlantıyı tekrar kullanmadan önce “Hey, orada mısın?” (SELECT 1) diyerek kontrol eder. Bu, veritabanı restart olduğunda uygulamanızın 500 hataları fırlatmasını engeller. Çok küçük bir performans maliyeti vardır ama sağladığı güvenilirlik paha biçilemez.
3. Bağlantı Sızıntıları (Connection Leaks)
“QueuePool Limit Reached” hatası alıyorsanız, ilk bakmanız gereken yer yük değil, kodunuzdur. Bir yazılımcının en büyük kabusu, kapatılmayan bağlantılardır (Orphan Connections). Eğer bir bağlantıyı close() etmeden fonksiyondan çıkarsanız, o bağlantı havuzda “Meşgul” olarak kalır ve sonsuza kadar kilitlenir.
Gelişmiş projelerde Context Manager yapısını (Bkz: Python Context Managers) kullanarak bunu otomatize etmelisiniz:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanager
def db_session():
"""Bağlantı sızıntılarını önleyen güvenli session yöneticisi."""
session = SessionLocal()
try:
yield session
session.commit()
except Exception as e:
session.rollback() # Hata varsa işlemi geri al
raise e
finally:
session.close() # Ne olursa olsun bağlantıyı havuza iade et!
4. Ölçeklenme Sorunu ve PgBouncer
Uygulamanız büyüdü, artık yüzlerce pod veya worker çalışıyor. SQLAlchemy pool’ları artık yetmiyor çünkü her uygulamanın kendi havuzu var ve toplam sayı veritabanını boğuyor. Burada devreye Database Proxy girer.
 PgBouncer, binlerce istemciyi az sayıda gerçek veritabanı bağlantısına multiplex eder.
PgBouncer, binlerce istemciyi az sayıda gerçek veritabanı bağlantısına multiplex eder.
PgBouncer, veritabanı ile uygulama arasına girerek bağlantıları yönetir. İki modu vardır:
- Session Pooling: İstemci bağlandığı sürece bağlantıyı tutar. (SQLAlchemy’ye benzer).
- Transaction Pooling: En verimli moddur. Bağlantı sadece bir transaction süresince tutulur. Transaction bittiği an bağlantı başka bir isteğe verilir. Bu sayede 10.000 eşzamanlı kullanıcıyı, arkada sadece 50 gerçek veritabanı bağlantısıyla yönetebilirsiniz. Bu, gerçekten sihir gibidir.
5. Caching vs Pooling: Farkı Anlamak
İkisi sık karıştırılır. Pooling, veritabanına giden yolu açık tutmaktır. Caching ise veritabanına gitmemektir. İkisini birlikte kullanmalısınız.
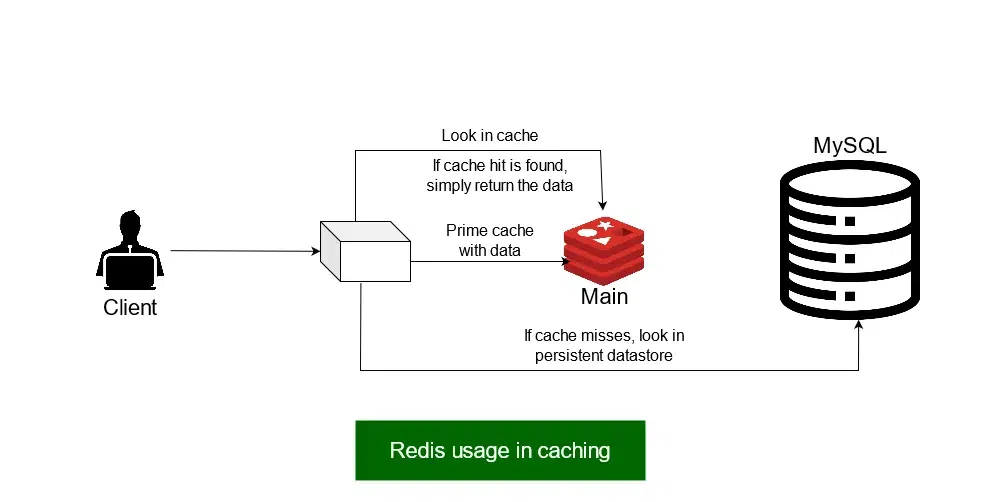 Redis ile önbellekleme stratejisi.
Redis ile önbellekleme stratejisi.
Sorgu sonucunu Redis’te tutmak (Caching), pool_size ihtiyacınızı azaltır. Ancak cache miss durumlarında sisteminizin hala sağlam bir pooling stratejisine ihtiyacı vardır.
6. Production Checklist: Canlıya Çıkmadan Önce
Senior bir mühendis olarak, kodunuzu production’a atmadan önce şu listeyi tiklemelisiniz:
- Pool Size Hesabı:
Pod Sayısı * (Pool + Overflow)değeriniz DB limitini aşıyor mu? - Pre-Ping:
pool_pre_ping=Trueaktif mi? - Timeouts: Uygulama tarafında
connect_timeout(DB’ye bağlanma süresi) vestatement_timeout(Sorgu süresi) ayarlı mı? Sonsuza kadar dönen sorgular havuzu kilitler. - Overflow:
max_overflowdeğeripool_size‘ın %50’sinden fazla olmamalı. Çok fazla overflow, connection thrashing’e (sürekli aç-kapa) neden olur. - Monitoring: Havuz doluluk oranını izliyor musunuz? (Prometheus/Grafana kullanarak
pool_checkout_countizlenmeli).
7. Sık Yapılan Hatalar (Anti-Patterns)
Yıllar içinde gördüğüm, performansı öldüren o klasik hatalar:
A. Havuzu Uygulama İçinde Yaymak
engine veya session_factory objesini her fonksiyonda yeniden oluşturmak. Doğrusu: Global bir singleton olarak bir kez tanımlayın ve tüm uygulama oradan alsın.
B. “Garbage Collection Temizler” Yanılgısı
“Bağlantıyı kapatmasam da Python sonunda temizler” diye düşünmek. Gerçek: GC çalışana kadar havuz kilitlenir. Asla GC’ye güvenmeyin, finally veya with kullanın.
C. Yanlış Timeout Ayarları
Veritabanı bağlantı süresini sonsuz yapmak. Eğer ağ koparsa, uygulamanız sonsuza kadar cevap bekleyen “zombi” bağlantılarla dolar. Önlem: connect_timeout=10 gibi agresif değerler kullanın.
8. Gerçek Hayat Senaryosu: “Idle Transaction” Krizleri
Bir fintech projesinde başımıza gelen olay: Yazılımcı arkadaşımız transaction başlatıyor, arada harici bir API’ye (kredi kartı servisi) istek atıyor ve sonra commit yapıyor. API 30 saniye gecikince, veritabanı bağlantısı 30 saniye boyunca “Idle in Transaction” durumunda bekliyor. Bu sırada tablo kilitli kalıyor.
Ders: Transaction bloğu içinde ASLA dış dünyaya (HTTP request, disk I/O) gitmeyin. İşinizi yapın, transaction’ı olabildiğince kısa tutun.
9. Terimler Sözlüğü (Glossary)
Teknik mülakatlarda veya mimari tartışmalarda işinize yarayacak kavramlar:
- Connection Thrashing: Sürekli yeni bağlantı açıp kapatarak sistemi yorma durumu.
- Starvation (Açlık): Havuzun tamamen dolu olması ve yeni gelen isteklerin bağlantı beklemesi.
- Hard Limit: Veritabanının config dosyasında (örn:
postgresql.conf) belirlenen fiziksel üst sınır. - Soft Limit: Uygulama tarafında belirlediğimiz havuz limiti. Soft limit her zaman Hard Limit’ten düşük olmalıdır.
- Multiplexing: Tek bir fiziksel kanaldan birden fazla mantıksal veri akışı geçirme (PgBouncer’ın yaptığı işlem).
Son Söz
Veritabanı optimizasyonu, sadece doğru index’i eklemek değildir. Verinin otobanda nasıl aktığını tasarlamaktır. Bağlantı havuzu, bu otobanın gişeleridir; gişeleri tıkarsanız, Ferrari hızında sorgularınız olsa bile trafik ilerlemez.
Her seferinde sıfırdan el sıkışmak yerine, açık kapıları kullanın. Sisteminiz size teşekkür edecektir.