Redis Desenleri: Sadece Cache Değil, Bir İsviçre Çakısı
Redis'i sadece 'SET key value' olarak mı kullanıyorsunuz? Sorted Sets, Pub/Sub, Geo ve HyperLogLog ile neler yapabileceğinizi keşfedin.
Birçok proje Redis’i sadece “Basit bir Cache” olarak kullanır. DB’den veriyi çek -> Redis’e koy -> Bir dahaki sefere Redis’ten al. Bu kullanım (“Cache-Aside Pattern”) en popüler kullanım olsa da, Redis’in yeteneklerinin sadece %10’udur. Redis bir “Key-Value Store” değil, bir “Data Structure Server”dır (Veri Yapısı Sunucusu). Listeler, kümeler, hashler, coğrafi veriler ve yayın akışları RAM hızında emrinizdedir. Bu yazıda, Redis’i sadece hızlandırıcı olarak değil, mimari bir bileşen olarak nasıl kullanabileceğinizi inceleyeceğiz.
 String, List, Set, Hash, ZSet ve kullanım alanları.
String, List, Set, Hash, ZSet ve kullanım alanları.
1. Caching Stratejileri: Cache-Aside vs Write-Through
Cache kullanmak kolaydır, zor olan “Cache Invalidation” (Önbellek geçersiz kılma)dır. İki ana strateji vardır:
Cache-Aside (Lazy Loading): Uygulamanız veriyi arar. Cache’te yoksa (Miss), gider DB’den alır ve Cache’e yazar.
- Artısı: Sadece ihtiyaç duyulan veri cache’e girer. Redis dolmaz.
- Eksisi: İlk istekte gecikme yaşanır. Cache Miss anında sistem yavaşlar (“Thundering Herd” problemi olabilir).
- Risk: “Stale Data” (Bayat Veri). DB güncellenirse Cache’in haberi olmaz. TTL (Time to Live) süresi bitene kadar eski veriyi görürsünüz.
Write-Through: Veriyi DB’ye yazarken AYNI ANDA Cache’e de yazarsınız.
- Artısı: Veri her zaman günceldir (Consistency). İlk okuma hızlıdır çünkü veri oradadır.
- Eksisi: Yazma işlemi yavaşlar (İki yere yazıyorsunuz). Hiç okunmayacak veriler bile Cache’te yer kaplar.
Genelde okuma ağırlıklı sistemlerde Cache-Aside kullanılır. Ancak “Thundering Herd” (Aynı anda binlerce isteğin cache’i boş görüp DB’ye saldırması) riskini önlemek için TTL Jitter kullanın. Yani her key’e 3600 saniye vermeyin; 3600 + random(0, 300) verin. Hepsi aynı anda expire olmasın.
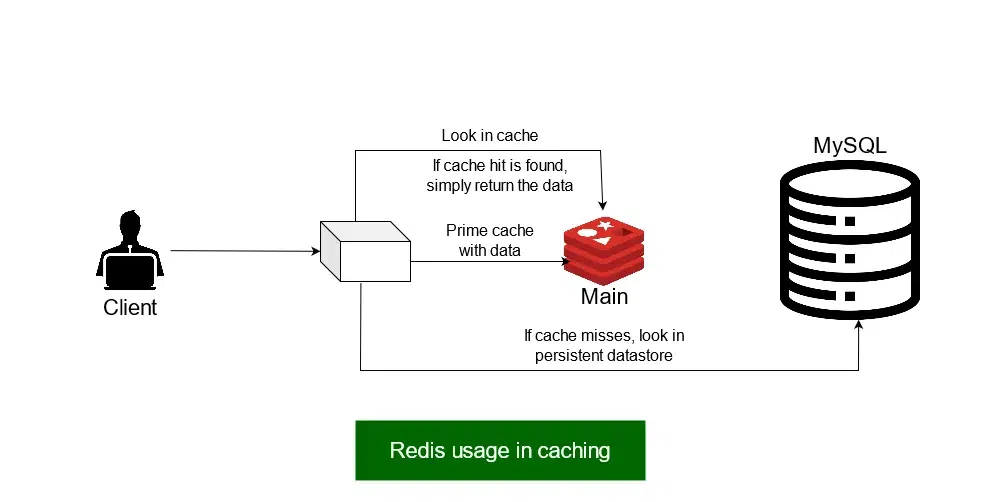 Application -> Cache (Miss) -> Database -> Cache (Set).
Application -> Cache (Miss) -> Database -> Cache (Set).
2. Gelişmiş Veri Yapıları ile Neler Yapılır?
Redis’i güçlü kılan şey, String dışındaki veri yapılarıdır.
Sorted Sets (ZSET): Oyun Liderlik Tablosu (Leaderboard) yapıyorsunuz. “En yüksek puanlı 10 oyuncuyu getir”. SQL ile milyonlarca satırı sıralamak zordur. Redis ZSET bu işi O(logN) ile yapar. ZADD leaderboard 500 "Ahmet" ve ZREVZRANGE leaderboard 0 9 ile anlık sıralama alırsınız.
HyperLogLog: 100 milyon “Tekil Ziyaretçi” sayacını Set ile tutmak GB’larca RAM yer. HyperLogLog ile sadece 12KB (Kilobyte!) harcayarak, %0.81 hata payıyla bu sayımı yapabilirsiniz.
GeoSpatial: “Bana en yakın 5 restoranı getir”. SQL’de Haversine formülüyle uğraşmayın. GEORADIUS komutuyla coğrafi sorguları milisaniyeler içinde yapın.
3. RedisOM: ORM Tadında Redis
Python’da Redis kullanırken json.dumps ile uğraşmak yerine RedisOM kullanın. Pydantic modellerini doğrudan Redis Hash’lerine eşler ve Redis Search ile sorgulama imkanı sunar.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from redis_om import HashModel, Field
class Customer(HashModel):
first_name: str = Field(index=True)
email: str
age: int = Field(index=True, sortable=True)
# Sorgula: Yaşı 20'den büyük olanlar
results = Customer.find(Customer.age > 20).all()
 RAM dolunca ne olacak? LRU, LFU ve Random silme stratejileri.
RAM dolunca ne olacak? LRU, LFU ve Random silme stratejileri.
4. Eviction Policies: RAM Dolunca Ne Olur?
Redis RAM’de çalışır, RAM dolarsa ne olacağını maxmemory-policy belirler:
allkeys-lru: En az kullanılanı sil (En popüler).volatile-lru: Sadece süresi (TTL) olanlardan en az kullanılanı sil.noeviction: Hata fırlat (Riskli).
5. Atomik İşlemler: Lua Scripting
Birden fazla komutu (Get + Incr + Set) bölünemez (Atomic) yapmak için Lua kullanın. Network gecikmesini (RTT) sıfıra indirir ve Race Condition’ı önler.
1
2
3
4
5
6
-- Basit bir Rate Limit scripti
local current = redis.call("INCR", KEYS[1])
if tonumber(current) == 1 then
redis.call("EXPIRE", KEYS[1], ARGV[1])
end
return current
6. Yayın Akışı: Pub/Sub vs Redis Streams
Pub/Sub, “Fire and Forget” mantığıyla çalışır. Dinleyici yoksa mesaj kaybolur. Redis Streams ise Kafka benzeri kalıcı bir log yapısıdır. Consumer Group desteği vardır, mesajlar diske yazılır ve kaybolmaz. Event-Driven mimariler için Streams kullanın.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Producer: Mesaj ekle
r.xadd("mystream", {"sensor_id": "1234", "temp": "19.8"})
# Consumer Group ile oku
try:
r.xgroup_create("mystream", "mygroup", id="0", mkstream=True)
except redis.exceptions.ResponseError:
pass
while True:
# Gruptan 1 mesaj oku
streams = r.xreadgroup("mygroup", "consumer1", {"mystream": ">"}, count=1)
if streams:
id, data = streams[0][1][0]
print(f"Data: {data}")
r.xack("mystream", "mygroup", id) # Onayla
7. Distributed Locking (Redlock)
Dağıtık sistemlerde aynı işin iki sunucuda çalışmasını önlemek için Kilit (Lock) mekanizması şarttır. set(nx=True, px=30000) komutu ile basit kilitler yapabilirsiniz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import redis
client = redis.Redis()
# 10 Saniyelik kilit. Context Manager otomatik release eder.
with client.lock("daily-report-job", timeout=10, blocking_timeout=1):
print("Rapor oluşturuluyor...")
# İş bitince kilit kalkar
8. Güvenlik: Redis’i Hardening Yapmak
Redis varsayılan olarak “Güvensiz” gelir (Şifresiz, her IP’ye açık). Production’da bu intihardır.
- ACL (Access Control Lists): Redis 6.0 ile geldi. Artık “default” user yerine kısıtlı kullanıcılar oluşturun.
ACL SETUSER worker on >pass123 ~cache:* +get +set-> Sadececache:ile başlayan keyleri okuyup yazabilir. - Rename Dangerous Commands:
FLUSHALLveyaKEYSgibi komutları geliştiricilerin yanlışlıkla çalıştırmasını engelleyin.rename-command FLUSHALL ""(Komutu tamamen siler). - TLS Encryption: Redis trafiği düz metindir (Plain Text). Araya giren biri (Man-in-the-Middle) verinizi okuyabilir. Mutlaka TLS/SSL açın.
9. High Availability: Sentinel vs Cluster
Redis tek sunucuda (Standalone) harikadır ama o sunucu yanarsa?
- Redis Sentinel: Master-Slave yapısını yönetir. Master çökerse, Slave’lerden birini yeni Master seçer (Failover). Yüksek Erişilebilirlik (HA) sağlar.
- Redis Cluster: Veriyi birden çok Master sunucuya böler (Sharding). Hem Yazma (Write) kapasitesini artırır hem RAM limitini aşmanızı sağlar. Kural: Veriniz tek RAM’e sığıyorsa Sentinel, sığmıyorsa Cluster kullanın.
Sonuç
Redis’i projenize dahil ettiğinizde sadece hız kazanmazsınız, mimari esneklik kazanırsınız. Kuyruk (Queue) yapabilirsiniz (List), Cache yapabilirsiniz (String), Pub/Sub ile chat uygulaması yazabilirsiniz, Liderlik tablosu yapabilirsiniz (ZSet). Ancak RAM’in uçucu olduğunu unutmayın. Sunucu kapanırsa veri gider (RDB/AOF persistence açsanız bile %100 garanti değildir).
Kalıcı verileriniz (Kullanıcılar, Siparişler, Faturalar) her zaman güvenli bir disk veritabanında (PostgreSQL vb.) durmalıdır. Redis hızlandırıcıdır, depolayıcı değil. Aradaki farkı bilmek, sisteminizin ayakta kalmasını sağlar.
Özetle:
- Cache-Aside pattern’i öğrenin ama risklerini bilin.
- ZSET ile sıralama problemlerini O(logN) hızında çözün.
- Lua scriptleri ile atomik işlemleri garanti altına alın.
- Redis Streams’i Kafka alternatifi olarak değerlendirin.
- Single Point of Failure olmaması için Sentinel veya Cluster mimarisini kurun.
- Kritik dağıtık işlemlerinizde Redlock algoritmasını kullanın.
Redis’i doğru kullandığınızda, sisteminizin performans darboğazlarını birer birer aştığını göreceksiniz.