Python Performans Optimizasyonu: Profiling Sanatı
Kodunuz yavaş mı çalışıyor? Tahmin yürütmeyin, ölçüm yapın. cProfile, py-spy ve memray ile darboğazları (bottleneck) tespit edin.
Donald Knuth’un o meşhur sözünü herkes bilir: “Erken optimizasyon, tüm kötülüklerin köküdür.” Ancak bu söz, yavaş kodu production’a atıp “sonra bakarız” demek için bir bahane değildir. Bir API endpoint’i 2 saniye sürüyorsa, kullanıcılarınız Knuth’un ne dediğini umursamaz; sekmeyi kapatıp gider.
Senior bir mühendis ile Junior arasındaki fark şudur: Junior “sanırım şurası yavaş” der ve rastgele kod değiştirir. Senior ise ölçer. Bu yazıda, Python kodunuzun röntgenini çeken araçları (Profiling) ve gerçek dünya optimizasyon tekniklerini inceleyeceğiz.
1. İlk Durak: cProfile ve SnakeViz
Python ile birlikte gelen (Built-in) cProfile, deterministik bir profilerdır. Yani kodunuzdaki her fonksiyon çağrısını tek tek sayar ve kaydeder.
Nasıl Kullanılır? Kodunuzu değiştirmeden terminalden çağırabilirsiniz:
1
python -m cProfile -o sonuc.prof app.py
Bu komut size binary bir dosya (sonuc.prof) verir. Okuması zordur. İşte burada devreye SnakeViz girer.
1
2
pip install snakeviz
snakeviz sonuc.prof
Tarayıcınızda açılan Sunburst (Güneş Patlaması) grafiği ile kodun en çok nerede vakit harcadığını saniyeler içinde görürsünüz. Genelde gördüğüm manzara şudur: Kodun %90’ı hızlıdır, ama utils.py içindeki tek bir regex işlemi işlemcinin %80’ini yiyordur.
2. Production’da Canlı Cerrahi: py-spy
cProfile iyidir ama kodu yavaşlatır (overhead). Canlıda (Production) çalışan bir Django veya FastAPI uygulamasını durdurmadan analiz etmek istiyorsanız, ihtiyacınız olan araç py-spy‘dır. Rust ile yazılmıştır ve çok düşük ek yük (overhead) ile çalışır. Sampling (örnekleme) yöntemi kullanır.
Top Modu: Linux top komutu gibi, o an en çok CPU tüketen fonksiyonları canlı izleyin:
1
2
# PID 1234 olan Python sürecini izle
sudo py-spy top --pid 1234
Record Modu (Flame Graph): 60 saniye boyunca sistemi izleyip, sonucunda o meşhur “Alev Grafiği”ni (Flame Graph) oluşturur.
1
sudo py-spy record -o profile.svg --pid 1234 --duration 60
Bu SVG dosyasını tarayıcıda açtığınızda, genişliği fazla olan (çok vakit harcayan) fonksiyonlar hemen göze çarpar. Eğer bir time.sleep veya lock.acquire üzerinde çok vakit harcanıyorsa, sorununuz CPU değil, I/O veya Threading’dir.
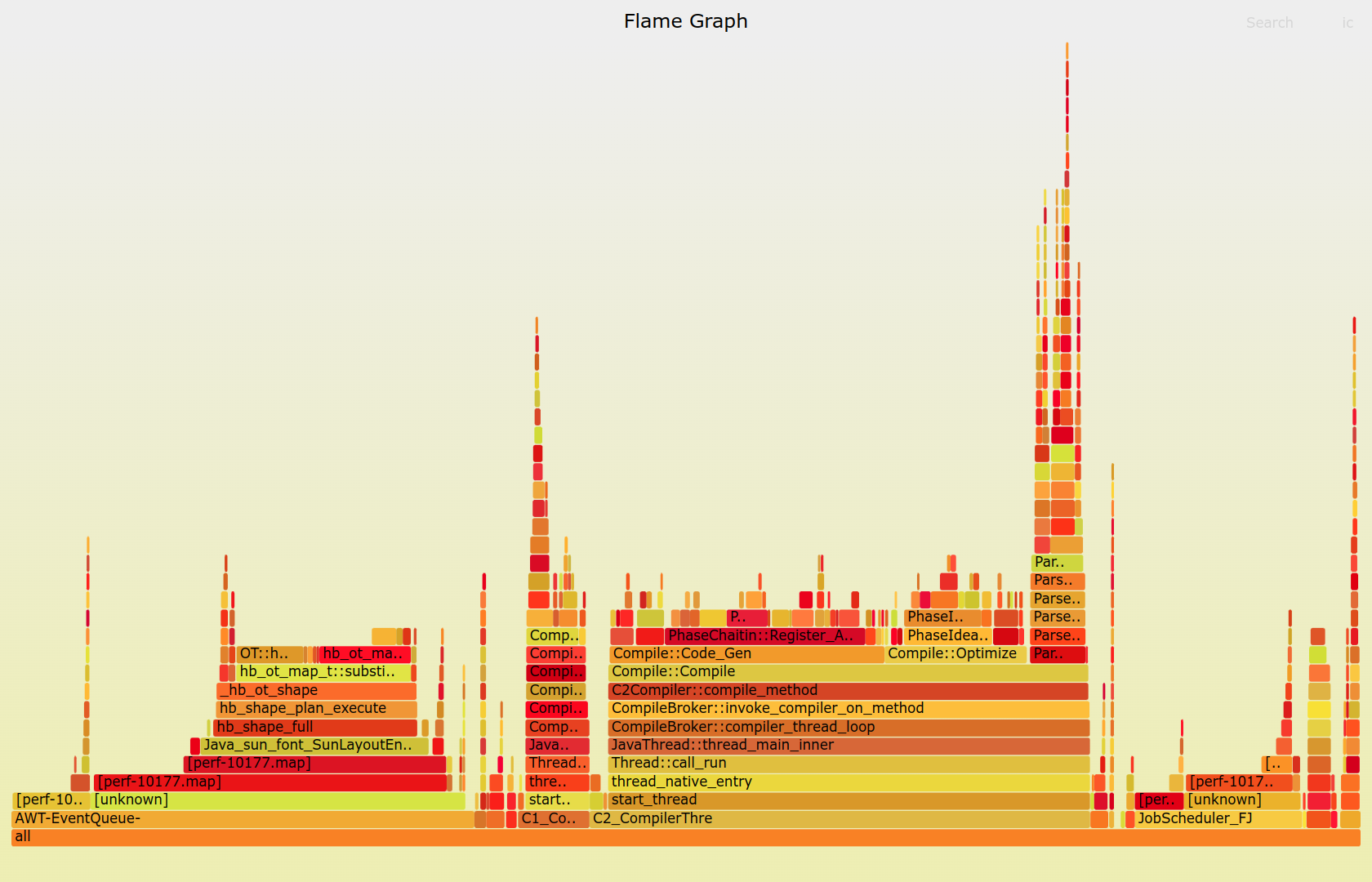 Alev grafiğinde geniş bloklar darboğazları (bottleneck) işaret eder.
Alev grafiğinde geniş bloklar darboğazları (bottleneck) işaret eder.
3. Bellek Sızıntıları (OOM) ve memray
“Python’da Garbage Collector var, memory leak olmaz” diyenler, C-Extension’ları (NumPy, Pandas, Pillow) kullananlardır. Bir Docker konteyneriniz sürekli OOM Killed (Out of Memory) hatası alıp yeniden başlıyorsa, suçlu muhtemelen global değişkenlerde unutulan listeler veya C seviyesindeki sızıntılardır.
Bloomberg’in geliştirdiği memray, şu an piyasadaki en iyi bellek analiz aracıdır.
1
2
3
4
5
# Bellek kullanımını kaydet
memray run -o memory.bin main.py
# Live mode (Canlı izleme)
memray run --live main.py
memray, hangi satırın kaç MB RAM ayırdığını (Allocation) ve bunu ne zaman serbest bıraktığını (Deallocation) gösterir.
4. Gerçek Suçlu Kim? Python mı, C mi, Sistem mi? (Scalene)
Bazen sorunun kaynağı Python kodunuz değildir. Scalene, CPU kullanımını üç kategoriye ayırarak size muazzam bir içgörü sağlar:
- Python Time: Sizin yazdığınız kod.
- Native Time: C kütüphaneleri (NumPy, RegEx vb.).
- System Time: Kernel işlemleri (Disk I/O, Network).
1
scalene app.py
Eğer sorununuz “Native Time”da ise, Python kodunu optimize etmekle vakit kaybetmeyin; algoritmayı veya kütüphaneyi değiştirin.
5. Düşük Maliyetli Optimizasyon Taktikleri
Darboğazı buldunuz, peki nasıl düzelteceksiniz? İşte en sık kullanılan reçeteler:
A. __slots__ Magic
Milyonlarca nesne (Object) oluşturuyorsanız, her nesne için bir __dict__ (dictionary) oluşturulur. Bu çok RAM yer. Class tanımına __slots__ ekleyerek %40-%50 RAM tasarrufu sağlarsınız.
1
2
3
4
5
class Point:
__slots__ = ['x', 'y'] # __dict__ oluşturulmaz
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
B. functools.lru_cache
Aynı girdilerle aynı çıktıyı veren ağır fonksiyonlarınız varsa (örn: recursive hesaplamalar veya statik konfigürasyon parse etme), bunları cacheleyin.
1
2
3
4
5
6
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=128)
def get_config(key):
# Pahalı dosya okuma işlemi...
return config[key]
D. String Interning
Eğer uygulamanızda milyarlarca kez tekrar eden stringler varsa (örn: JSON keyleri, status kodları), bunları “intern” ederek RAM’den tasarruf edebilirsiniz. Python, değişken adları için bunu otomatik yapar ama dinamik stringler için manuel yapmalısınız.
1
2
3
4
import sys
s1 = sys.intern("status_active")
s2 = sys.intern("status_active")
print(s1 is s2) # True (Aynı hafıza adresi)
E. List Comprehension vs Loop
Bu klasik bir tavsiyedir ama nedenini bilmek önemlidir. List comprehension, C seviyesinde optimize edilmiş bir döngüdür. Python bytecode yorumlayıcısı (interpreter) daha az çalışır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Yavaş
res = []
for i in range(1000):
res.append(i * 2)
# Hızlı (%20-%30)
res = [i * 2 for i in range(1000)]
Ancak dikkat: filter ve map fonksiyonları, lambda ile kullanıldığında List Comprehension’dan yavaş olabilir. Profiling yapmadan değiştirmeyin!
6. Tahmin Etme, Ölç: pytest-benchmark
Bir optimizasyon yaptınız, “daha hızlı oldu” hissi yeterli değildir. Kanıtlamanız lazım. pytest-benchmark eklentisi ile kodunuzun öncesini ve sonrasını istatistiksel olarak karşılaştırabilirsiniz.
1
2
3
def test_my_function(benchmark):
result = benchmark(my_function)
assert result == expected
Bu size Min, Max, Mean ve StdDev değerlerini verir. Eğer ortalamanız düşmüş ama StdDev artmışsa, kodunuz stabil değildir.
7. Production Checklist: Sürekli İzleme (Continuous Profiling)
Sadece kriz anında değil, her zaman izlemelisiniz. Büyük sistemlerde (Datadog, Sentry Profiling, Pyroscope) “Continuous Profiling” açmak, size “Dün attığımız deploydan sonra Login servisi %15 daha fazla CPU kullanmaya başladı” gibi hayati trendleri gösterir.
 Doğru iş için doğru araç: CPU için py-spy, RAM için memray.
Doğru iş için doğru araç: CPU için py-spy, RAM için memray.
Özetle
- Bilinmeyen kod optimize edilmez. Önce cProfile veya py-spy ile darboğazı bulun.
- Memory sorunları için memray kullanın.
- Data Science işlerinde Scalene ile C/Python ayrımını yapın.
- Optimizasyonlarınızı pytest-benchmark ile kanıtlayın.
Hızlı kod yazmak bir ego tatmini değil, kaynak (para) ve zaman tasarrufu sanatıdır.