API Throttling: Sunucunuzu DDoS ve Kötü Niyetten Koruyun
API'nizi dünyaya açtınız, peki ya biri saniyede 1000 istek atarsa? Token Bucket algoritması, Redis ve FastAPI ile hız sınırlama.
Bir API geliştirdiğinizde varsayılan olarak “sınırsız” güvene sahipsinizdir. “İstemci mantıklı davranır, ihtiyacı kadar ister” diye düşünürsünüz. Ama gerçek dünya böyle değildir. Hatalı yazılmış bir while(true) döngüsü (Friendly Fire), meraklı bir pentester veya kötü niyetli bir rakip (DDoS), sunucunuzu dakikalar içinde “Unresponsive” hale getirebilir.
API Rate Limiting (Hız Sınırlama), sadece güvenlik değil, aynı zamanda “Adil Kullanım” (Fairness) ve “Maliyet Kontrolü” (Cost Management) için de gereklidir. Bir kullanıcının tüm CPU gücünü sömürmesine izin veremezsiniz. Bu yazıda, kendi Rate Limiter’ımızı tasarlayacağız, Redis Lua Scripting ile atomikliği sağlayacağız ve FastAPI middleware entegrasyonunu yapacağız.
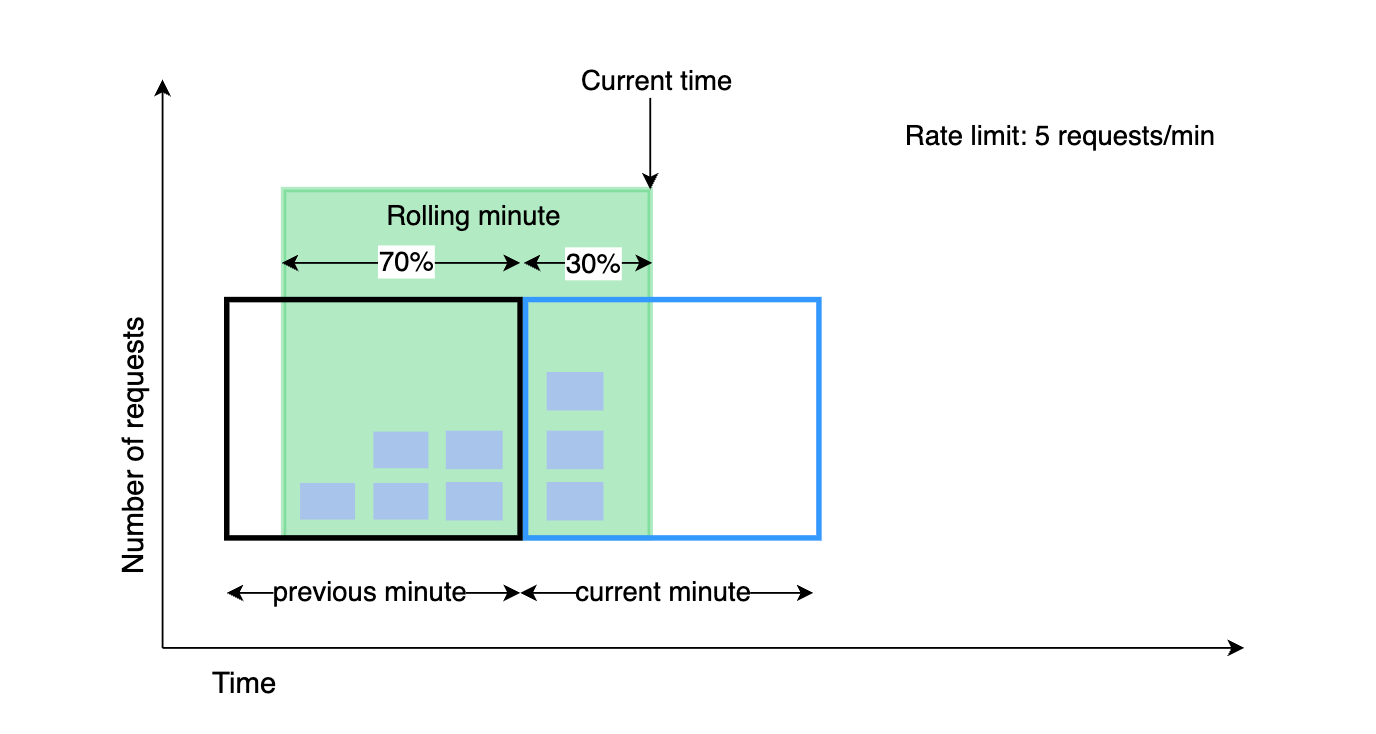 Token Bucket, Leaky Bucket ve Fixed Window algoritmaları.
Token Bucket, Leaky Bucket ve Fixed Window algoritmaları.
1. Algoritmalar: Token Bucket vs Fixed Window
Rate Limiting denince akla birkaç algoritma gelir. Hangisini seçeceğiniz, kullanım senaryonuza bağlıdır.
Fixed Window (Sabit Pencere): “Her dakika 100 istek”. Saat 12:00:00’da sayaç sıfırlanır.
- Sorun: 12:00:59’da 100 istek, 12:01:00’da 100 istek daha gelirse, 2 saniyede 200 istek işlersiniz. Sunucu anlık yükten (Spike) çökebilir.
Sliding Window (Kayan Pencere): Pencere sabittir ama kayarak ilerler. “Son 60 saniyedeki istek sayısı”. Daha adildir ama hesaplaması daha maliyetlidir (Redis Sorted Set gerekir).
Token Bucket (Jeton Kovası): En popüler ve esnek algoritmadır (AWS, Stripe bunu kullanır). Bir kovanız var. Her saniye içine 5 jeton düşüyor. Kapasitesi 100. Kullanıcı istek atınca kovadan 1 jeton alır. Kova boşsa “429 Too Many Requests” döner.
- Avantajı: “Burst” (Anlık patlama) trafiğe izin verir. Kova doluysa aynı anda 100 istek atılabilir, sonra dolması beklenir.
2. Redis ve Lua ile Atomic Rate Limiter
Uygulamanız dağıtık (Distributed) çalışıyorsa, in-memory (RAM) sayaç kullanamazsınız. Ortak bir Redis’e ihtiyacınız var. Ancak standart Redis komutları (GET sonra INCR) arasında “Race Condition” oluşabilir. İki istek aynı anda GET yapıp ikisi de limitin altında olduğunu sanabilir.
Çözüm: Lua Scripting. Redis’te Lua scriptleri atomik çalışır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import redis
r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
# Token Bucket Lua Script
# KEYS[1]: user_key, ARGV[1]: refill_rate, ARGV[2]: capacity, ARGV[3]: now
lua_script = """
local tokens = tonumber(redis.call("get", KEYS[1]) or ARGV[2])
local last_refill = tonumber(redis.call("get", KEYS[1] .. ":ts") or ARGV[3])
local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2])
local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local now = tonumber(ARGV[3])
local delta = math.max(0, now - last_refill)
local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, tokens + (delta * rate))
if filled_tokens >= 1 then
redis.call("set", KEYS[1], filled_tokens - 1)
redis.call("set", KEYS[1] .. ":ts", now)
return 1 -- İzin ver
else
return 0 -- Engelle
end
"""
limiter = r.register_script(lua_script)
Bu script ile binlerce concurrent istek gelse bile sayaç şaşmaz.
3. FastAPI Entegrasyonu (Dependency Injection)
Python’un modern framework’ü FastAPI’de bunu bir “Dependency” olarak kullanmak çok şıktır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends, HTTPException, Request
from starlette.status import HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS
import time
app = FastAPI()
def rate_limiter(request: Request):
user_ip = request.client.host
limit_key = f"rate_limit:{user_ip}"
# Saniyede 0.5 jeton (2 saniyede 1), Kapasite 10
allowed = limiter(keys=[limit_key], args=[0.5, 10, time.time()])
if not allowed:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS,
detail="Rate limit exceeded. Try again later."
)
@app.get("/api/dashboard", dependencies=[Depends(rate_limiter)])
async def get_dashboard():
return {"data": "Super Secret Metrics"}
Bu sayede business logic (fonksiyonun içi) tertemiz kalır. Rate limiting, altyapısal bir katman (Middleware) olarak çalışır.
4. İstemci Tarafı: Jitter ve Exponential Backoff
Sunucunuz 429 döndüğünde, istemci (mobil app) ne yapmalı? Hemen tekrar denerse (Retry Storm), sunucuyu daha da boğar. Doğru yaklaşım Exponential Backoff (Üstel Bekleme) ve Jitter (Rastgelelik) eklemektir.
- Hata al -> 1sn bekle.
- Hata al -> 2sn bekle.
- Hata al -> 4sn bekle.
- Hata al -> 4sn + random(0.1, 1.0)sn bekle (Jitter).
Jitter sayesinde, binlerce istemcinin aynı anda tekrar denemesini (Thundering Herd) engellersiniz.
5. İleri Seviye: Katmanlı Limitler (Tiering)
Her kullanıcı eşit değildir.
- Free: 10 req/min
- Pro: 1000 req/min
- Enterprise: Sınırsız
Bu limitleri kodda if/else ile değil, veritabanında veya Redis’te tutmalısınız. Dependency içinde kullanıcının API Key’ine bakıp, ona özel limiti çekerek Lua scriptine argüman olarak verin.
1
2
3
user_tier = get_user_tier(api_key) # Redis'ten çek
capacity = TIER_LIMITS[user_tier]
allowed = limiter(keys=[key], args=[refill_rate, capacity, now])
Bu yapı, SaaS ürünlerinde “Upsell” (Üst paket satışı) için kritik bir mekanizmadır.
6. Monitoring ve Alerting
Rate Limiter’ınızın sessizce çalışması yetmez, onu izlemelisiniz. Sürekli limitlere takılan bir IP varsa, bu bir DDoS saldırısı olabilir. Prometheus ile rate_limit_hits_total metriği tutun ve Grafana’da görselleştirin. Eğer 429 hataları aniden %500 artarsa, Slack’ten bildirim almalısınız.
7. IP Adresi Yeterli mi? (Spoofing ve NAT)
Çoğu tutorial “IP bazlı” limitlerden bahseder ama bu production için tehlikelidir.
- NAT: Bir üniversite kampüsündeki 1000 öğrenci aynı dış IP’den çıkış yapar. IP’yi engellerseniz masum kullanıcıları da yakarsınız.
- VPN/Proxy: Saldırgan IP’sini sürekli değiştirebilir.
Çözüm: Daima API Key veya User ID (JWT) üzerinden limit uygulayın. IP limitini sadece “Login” gibi kimliksiz endpointlerde (Brute-Force koruması) kullanın.
8. Rate Limiting bir Circuit Breaker mıdır?
Tam olarak değil ama kardeştirler. Rate Limiter, “Kapıdaki Bekçi”dir. İçeri giren istek sayısını sınırlar. Circuit Breaker ise “Sigorta”dır. İçerideki bir servis (örn. Veritabanı) çökerse, akımı keser. Ancak agresif bir Rate Limiting, veritabanınızın aşırı yük altında ezilmesini önleyerek dolaylı yoldan bir sigorta görevi görür. Veritabanı CPU’su %90’a vurduğunda, Rate Limit’i dinamik olarak sıkılaştıran (Adaptive Grotling) sistemler “Google Site Reliability Engineering” kitabında önerilen advanced bir tekniktir.
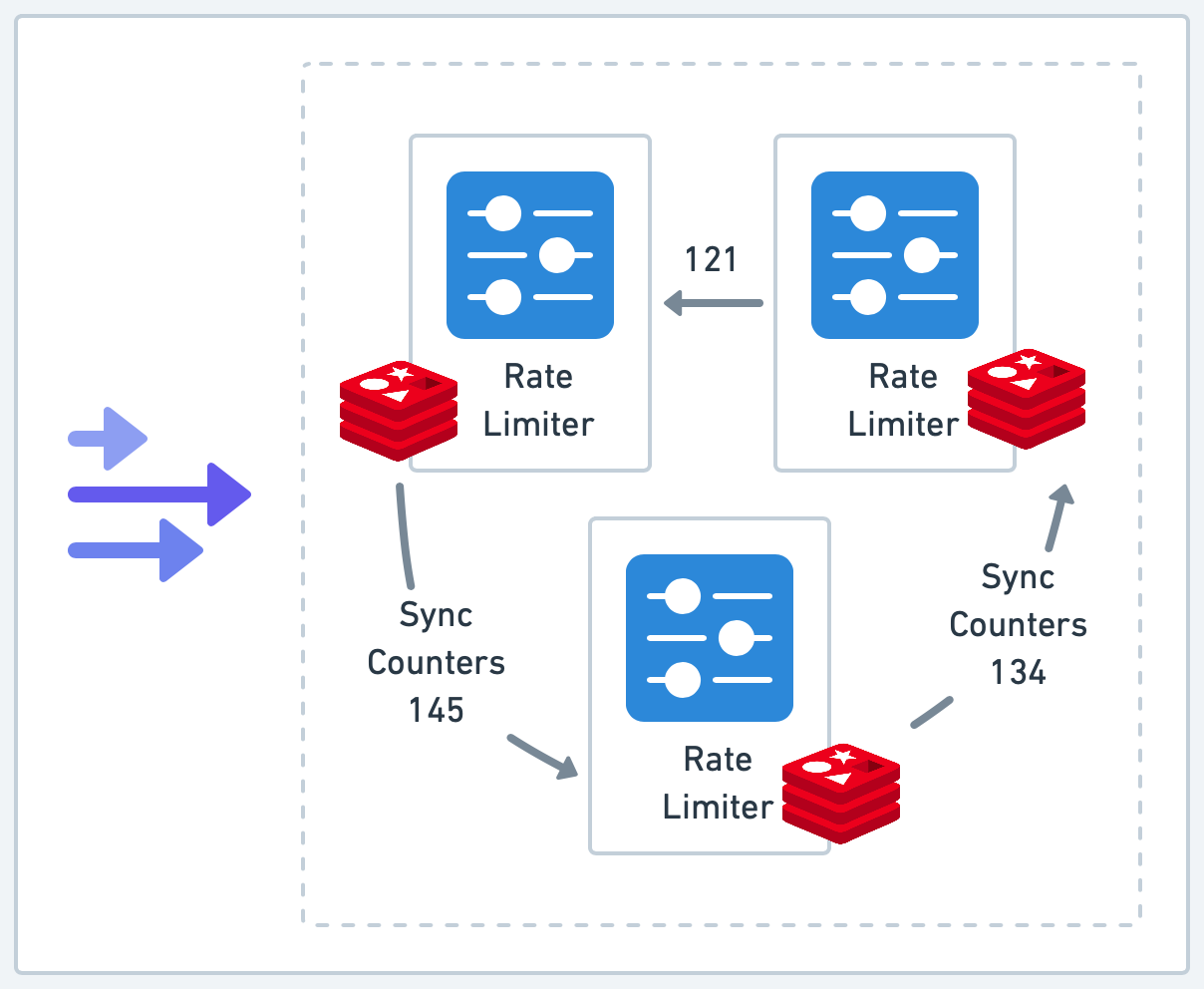 Çoklu uygulama sunucusu ve merkezi Redis sayacı.
Çoklu uygulama sunucusu ve merkezi Redis sayacı.
Sonuç
Rate Limiting, API’nizin emniyet kemeridir. Kullanıcılarınızın yanlışlıkla (veya kasten) servisinizi çökertmesini engeller. Yükü tahmin edilebilir (predictable) hale getirir. Redis ve Lua Scripting ikilisi, bu iş için endüstri standardıdır. Unutmayın, en iyi API, ayakta kalan API’dir. Eğer Nginx kullanıyorsanız (limit_req_zone), en dış katmanda kaba bir koruma, içeride ise (FastAPI+Redis) hassas ve kullanıcı bazlı koruma yaparak “Defense in Depth” (Derinlemesine Savunma) ilkesini uygulayın.