Python AsyncIO: Senior Geliştiricinin Hayatta Kalma Rehberi
asyncio.gather() öldü, yaşasın TaskGroup! Event Loop'u bloklamadan senkron kodu nasıl çalıştırırsınız? uvloop ve yappi ile performans notları.
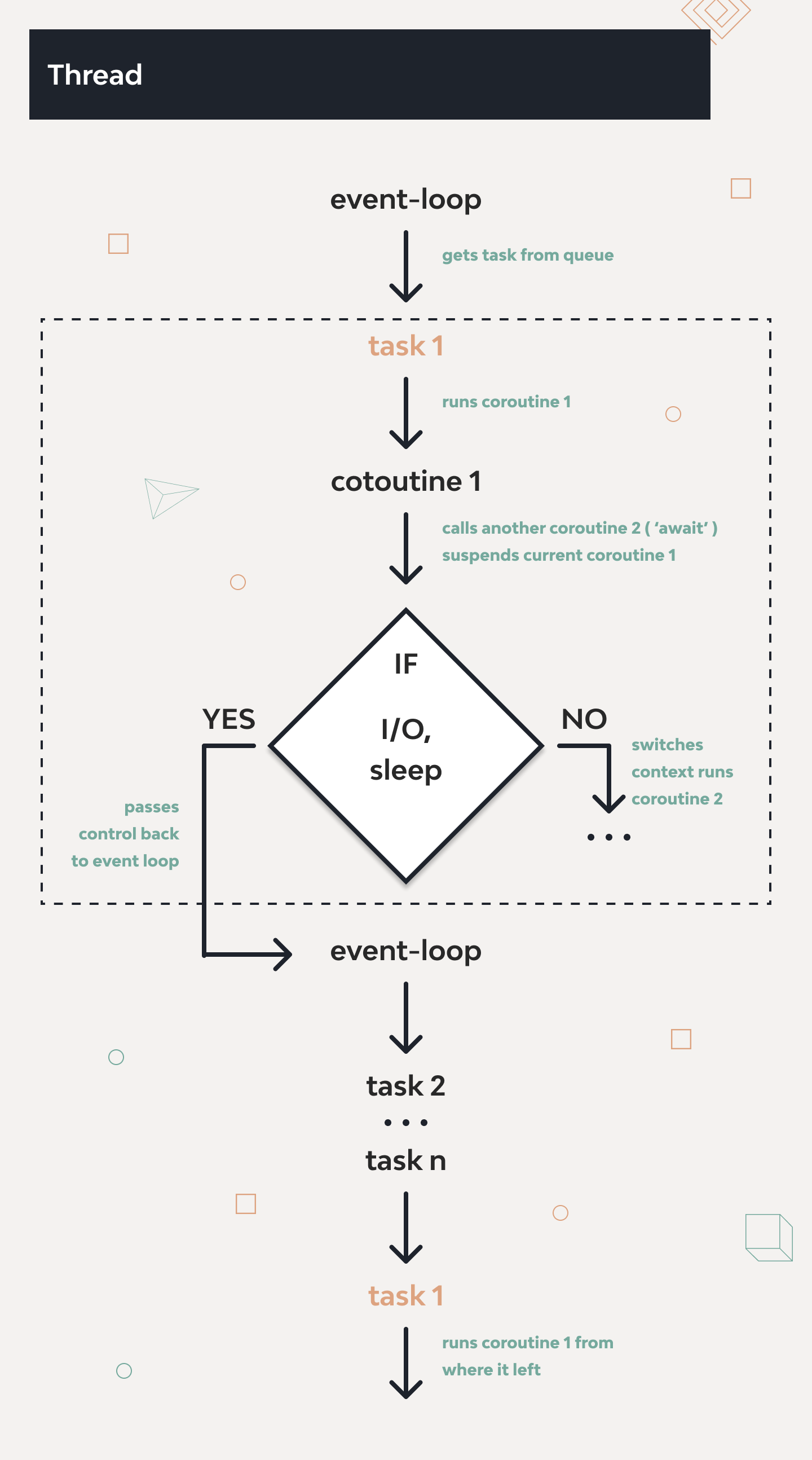
Python’da async/await yazmak kolaydır. Zor olan, tüm sistemin tek bir veritabanı sorgusu yüzünden (blocking IO) kilitlendiği anı debug etmektir.
Bu yazıda “Hello World” örneklerini geçip, production ortamında AsyncIO ile başa çıkma sanatını konuşacağız.
1. Modern Concurrency: asyncio.gather Öldü!
Yıllarca asyncio.gather() kullandık. Ama bir sorun vardı: Görevlerden biri hata verirse diğerleri ne olacak? (Hepsini iptal mi edelim, devam mı edelim?). Yönetmesi zordu.
Python 3.11 ile gelen Structured Concurrency (TaskGroup) bu sorunu kökten çözdü.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import asyncio
async def main():
try:
async with asyncio.TaskGroup() as tg:
tg.create_task(servis_a_cagir())
tg.create_task(servis_b_cagir())
except Exception as e:
print(f"Bir hata oldu, diğer tüm görevler iptal edildi: {e}")
TaskGroup context manager’ı, içindeki bir görev hata verirse diğerlerini otomatik iptal eder (cancel). Bu, “arkada unutulan zombi task” problemini bitirir.
2. Ölümcül Günah: Event Loop’u Bloklamak
Async dünyasında en büyük suç, Event Loop içinde senkron (bloklayıcı) kod çalıştırmaktır.
1
2
3
4
# YANLIŞ: Tüm sunucuyu dondurur!
async def veri_getir():
time.sleep(5) # Event loop 5 saniye durdu. Kimseye cevap yok.
return "bitti"
Eğer elinizde eski bir kütüphane varsa (Örn: standart requests veya eski SQLAlchemy), onu asyncio.to_thread() ile sarmalamalısınız (Python 3.9+).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import asyncio
import requests
async def legacy_api_cagir():
# Bu satır blocking kodu ayrı bir thread'e atar.
# Event loop bloklanmaz!
response = await asyncio.to_thread(requests.get, "https://api.eski.com")
return response.json()
3. Performans Hilesi: uvloop
Python’ın standart event loop’u pure-python’dır ve fena değildir. Ama Node.js veya Go hızı istiyorsanız, uvloop kurun. uvloop, C ile yazılmış (libuv) ve standart loop’tan 2-4 kat daha hızlı bir drop-in replacement’tır.
1
pip install uvloop
1
2
3
4
5
6
import asyncio
import uvloop
# Tek satırda hız artışı
uvloop.install()
asyncio.run(main())
FastAPI ve uvicorn bunu varsayılan olarak zaten kullanır.
4. Debugging: “Loop Neden Durdu?”
Async kodunuz yavaşsa, standart cProfile size yalan söyler. Çünkü await sırasında geçen süreyi “fonksiyon çalışıyor” sanır.
İhtiyacınız olan araç: Yappi veya Py-Spy. Özellikle Development modunda, Event Loop’un debug modunu açarak bloklayan kodları görebilirsiniz:
1
2
# Bloklayan call varsa konsola uyarı basar
asyncio.run(main(), debug=True)
Log çıktısı: Executing <Task...> took 0.500 seconds. Bu uyarıyı görüyorsanız, o fonksiyona to_thread yapmanız gerekir.
5. Büyük Veri: Async Generators (async for)
Milyonlarca satırlık bir veritabanı tablosunu çekerken RAM’i şişirmek istemezsiniz. Senkron dünyada yield kullanırdık. Asenkron dünyada ise async yield.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
async def fetch_pages(url):
page = 1
while True:
resp = await client.get(f"{url}?page={page}")
if not resp.data:
break
yield resp.data # Veriyi parça parça akıt
page += 1
async def main():
async for item in fetch_pages("https://api.buyukveri.com"):
print(f"İşleniyor: {item}")
Bu yöntemle 10GB veriyi, sadece 100MB RAM harcayarak işleyebilirsiniz.
6. Kibar Olun: Semaphore ile Rate Limiting
asyncio o kadar hızlıdır ki, dikkatsiz kodlarsanız kendi API’nize DDoS saldırısı yapabilirsiniz. 10.000 isteği aynı anda atarsanız sunucu çöker.
Frenlemek için Semaphore kullanılır:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
sem = asyncio.Semaphore(10) # Aynı anda sadece 10 işçi çalışsın
async def safe_request(url):
async with sem: # Kapıda bekle, içeride 10 kişi varsa girme
return await client.get(url)
# 1000 istek de olsa, aynı anda sadece 10'u aktiftir
tasks = [safe_request(url) for url in urls]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
7. Test Edilebilirlik: pytest-asyncio
Async kodu test etmek, asyncio.run() çağırmaktan ibaret değildir. pytest‘in asenkron eklentisini kurmalısınız.
1
pip install pytest-asyncio
1
2
3
4
5
6
import pytest
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_my_api():
result = await my_async_function()
assert result == "success"
Mocking yaparken de AsyncMock kullanmayı unutmayın. Standart MagicMock await edilemez.
8. Hata Yönetimi: ExceptionGroup
Python 3.11 ile gelen ExceptionGroup, birden fazla hata fırlatıldığında (örneğin TaskGroup içinde 3 task aynı anda patlarsa) hepsini yakalamanızı sağlar.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
try:
async with asyncio.TaskGroup() as tg:
tg.create_task(task1())
tg.create_task(task2())
except* ValueError as eg:
print(f"Value Errorlar: {eg.exceptions}")
except* NetworkError as eg:
print(f"Network Errorlar: {eg.exceptions}")
Bu sözdizimi (except*), asenkron hata yönetiminde devrimdir.
9. Görev Kontrol: aiomonitor
Production’da çalışan bir kodunuz kilitlendi. Nerede takıldığını nasıl anlarsınız? aiomonitor, çalışan event loop’a Telnet ile bağlanıp, o an hangi coroutine’lerin çalıştığını görmenizi sağlar. Python’ın asenkron “top” komutu gibidir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
import aiomonitor
async def main():
# 50101 portundan telnet sunucusu açar
with aiomonitor.start_monitor(loop=loop):
await uygulama_baslat()
10. Production Checklist
- ORM Seçimi: Tamamen asenkron sürücü kullanın (SQLAlchemy
AsyncSession+asyncpg). - HTTP Client:
requestsyerinehttpxveyaaiohttpkullanın. - Timeout: Her dış çağrıya mutlaka timeout verin.
await asyncio.wait_for(coro, timeout=5.0). Sonsuza kadar bekleyen bir socket, worker’ı öldürür. - Graceful Shutdown: SIGTERM sinyali gelince
TaskGroupiçindeki işleri nazikçe iptal ediyor musunuz? - Logging: Asenkron loglama için
aiologgerkullanıyor musunuz? (Disk I/O bile loop’u bloklayabilir). - Shielding: Kritik işleriniz iptal edilmesin istiyorsanız
asyncio.shield()ile koruyor musunuz?
Özetle
AsyncIO sihirli bir değnek değildir. CPU bound (Matematiksel) işlemlerde size hız kazandırmaz (onun için multiprocessing gerekir). Ancak IO bound (Web, DB) işlerde, tek bir çekirdekte binlerce isteği yönetmenizi sağlar.
Kural basit: Loop dönmeli. Onu asla durdurmayın.