MongoDB ve NoSQL: İlişkisel Dünyadan Kaçış ve Şema Tasarımı
SQL alışkanlıklarınızı kapıda bırakın. MongoDB'de Embedding vs Referencing, Schema Validation ve Aggregation Pipeline ile veriyi özgür bırakın.
Yıllarca RDBMS (MySQL, PostgreSQL) kullandıktan sonra MongoDB’ye geçtiğinizde ilk hatayı muhtemelen yapacaksınız: İlişkisel veritabanı gibi şema tasarlamak. “Kullanıcılar tablosu olsun, siparişler tablosu olsun, bunları user_id ile joinleyelim.” Eğer bunu yapacaksanız, MongoDB kullanmayın. PostgreSQL sizin için daha iyi bir seçenek.
MongoDB’nin gücü, veriyi “kullanıldığı gibi” saklamasından gelir. SQL’de Normalization (Veriyi bölme) kraldır. MongoDB’de ise Access Patterns (Veriye erişim şekli) kraldır. JOIN pahalıdır (hatta dağıtık sistemlerde imkansızdır). MongoDB ise veriyi Embedded (Gömülü) tutarak bu maliyeti sıfıra indirir. Bu yazıda, “Data together, accessed together” (Birlikte kullanılan veri, birlikte saklanır) prensibini, Şema Validasyonunu ve ACID Transaction yanlışlarını inceleyeceğiz.
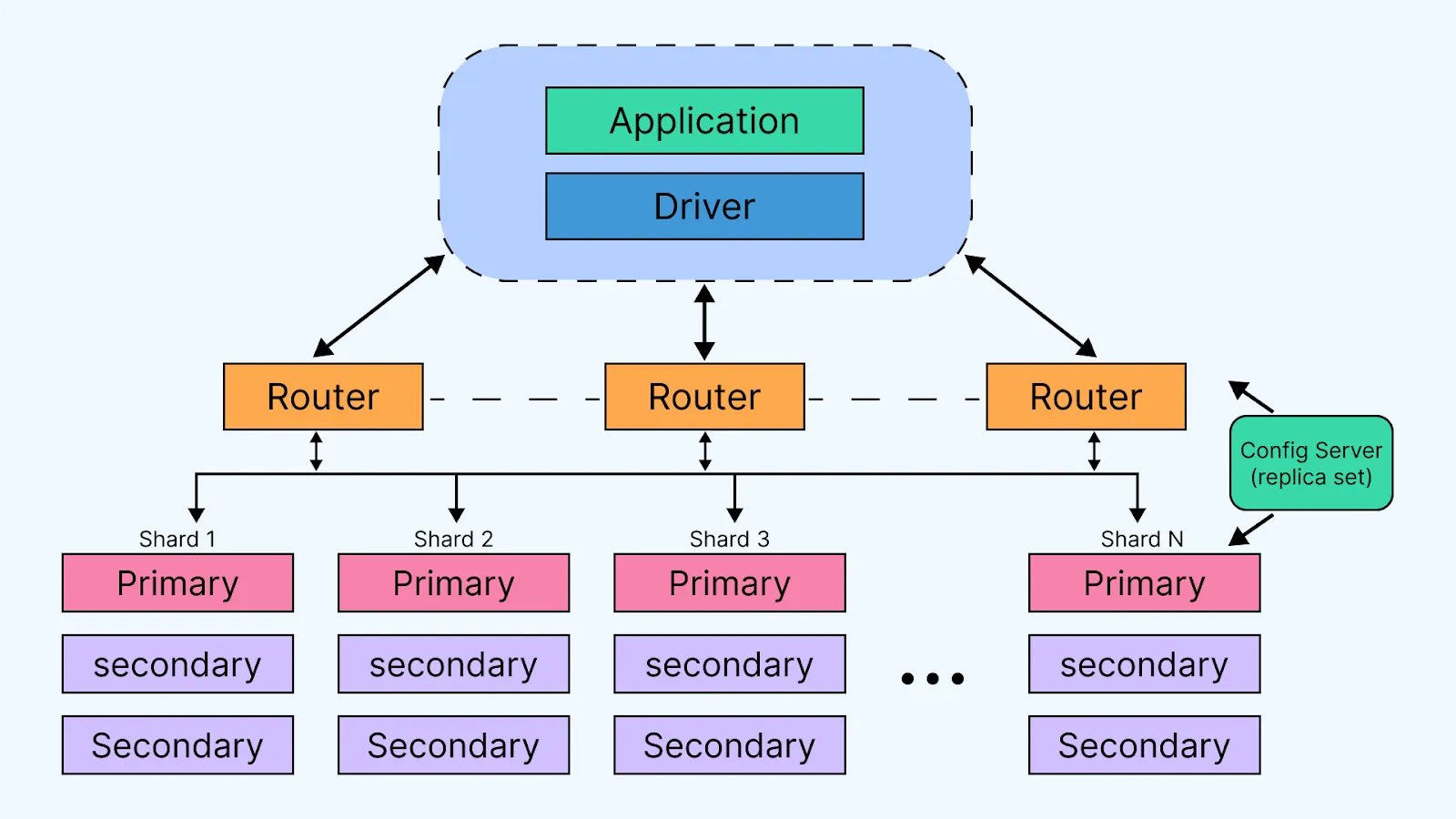 Rigid Schema (SQL) vs Flexible Document (NoSQL) yapısı.
Rigid Schema (SQL) vs Flexible Document (NoSQL) yapısı.
1. Embedding vs Referencing: Karar Matrixi
MongoDB tasarımındaki en kritik soru: “Veriyi gömmeli miyim (Embed), yoksa referans mı vermeliyim (Reference)?”
Embedding (Denormalization): Bir blog yazısı ve yorumları düşünün. Bir yazı gösterilirken %99 ihtimalle yorumları da gösterilir. SQL’de posts ve comments tabloları yapıp JOIN atarsınız. MongoDB’de ise comments dizisini post dokümanının içine gömersiniz.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Post Document
{
"_id": "...",
"title": "MongoDB Tips",
"comments": [
{ "user": "Ahmet", "text": "Harika!" },
{ "user": "Ayşe", "text": "Teşekkürler." }
]
}
Tek bir disk okuması (IO) ile tüm veriyi alırsınız. Network gecikmesi (Latency) minimumdur.
- Kural: “One-to-Few” ilişkilerde Embed kullanın.
Referencing (Normalization): Eğer veri “Unbounded” (Sınırsız) büyüyorsa veya “Many-to-Many” ilişki varsa referans kullanın. Örneğin bir e-ticaret sitesinde ürünler ve kategoriler. Kategori adı değişince 1 milyon ürünü update etmek istemezsiniz. Veya bir Instagram fenomeninin takipçileri; bir dökümanın içine 5 milyon UserID gömemezsiniz (16MB Limit).
- Kural: “One-to-Many” veya “Many-to-Many” ilişkilerde Reference kullanın.
2. Schema Validation: “Şemasız” Efsanesi
“MongoDB şemasızdır (Schemaless), kafama göre veri atarım, hızlı geliştiririm.” Bu, projenin 6. ayında patlamasına neden olan, Jr. Developer yanılgısıdır. Evet, MongoDB şemayı zorlamaz (enforce etmez) ama uygulamanızın (Backend) bir şema beklentisi vardır. email alanı string olmalıdır, age integer olmalıdır. Veritabanında bozuk veri (Garbage Data) varsa, kodunuz KeyError ile patlar.
MongoDB 3.6+ ile gelen JSON Schema Validation ile kuralları DB seviyesinde koyabilirsiniz:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
db.createCollection("users", {
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: [ "name", "email", "address" ],
properties: {
name: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "İsim alanı zorunludur"
},
email: {
bsonType: "string",
pattern: "^.+@.+$", // Regex desteği
description: "Geçerli bir email olmalı"
},
age: {
bsonType: "int",
minimum: 18,
description: "Yetişkin olmalı"
}
}
}
},
validationLevel: "strict", // Eski veriyi bozmaz, yeni veriyi reddeder
validationAction: "error"
})
Bu kuralı koyduktan sonra, hiçbir geliştirici (veya bug’lı kod) veritabanına emailsiz user ekleyemez.
3. İndeksleme Stratejileri: ESR Kuralı
Sorgularınız yavaş mı? explain("executionStats") yapıp COLLSCAN (Collection Scan) görüyorsanız geçmiş olsun. Tüm tablo taranıyor demektir. Birleşik (Compound) indeks oluştururken, alanların sırası hayati önem taşır. ESR Kuralı (Equality, Sort, Range):
- Equality (Eşitlik):
status: "active"gibi tam eşleşme yapan alanlar en başa. - Sort (Sıralama):
sort({ createdAt: -1 })gibi sıralama alanları ortaya. - Range (Aralık):
price: { $gt: 100 }gibi aralık sorguları sona.
Hatalı İndeks: { price: 1, status: 1 } Sorgu: find({ status: "active" }).sort({ price: 1 }) Bu indeks verimsizdir! Çünkü önce range (price) var, sonra equality (status). MongoDB, statusu bulmak için tüm fiyat aralığını taramak zorunda kalır.
 Compound Index ve ESR kuralı ile sorgu optimizasyonu.
Compound Index ve ESR kuralı ile sorgu optimizasyonu.
4. Aggregation Pipeline: SQL’den Güçlü Mü?
Eskiden “MapReduce” vardı, yavaştı. Artık Aggregation Framework var ve SQL’in GROUP BY yeteneklerinden çok daha esnek. Linux pipe (|) mantığıyla çalışır. Veri bir aşamadan (Stage) girer, işlenir ve sonrakine aktarılır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
db.orders.aggregate([
// 1. Filtrele (Index kullanır, hızlıdır)
{ $match: { status: "completed", date: { $gte: ISODate("2023-01-01") } } },
// 2. Müşteri bazında grupla ve toplam tutarı hesapla
{ $group: { _id: "$customerId", totalAmount: { $sum: "$amount" }, count: { $sum: 1 } } },
// 3. 1000 TL üzeri harcayanları al (HAVING)
{ $match: { totalAmount: { $gt: 1000 } } },
// 4. Diğer koleksiyondan (users) müşteri adını çek (JOIN)
{ $lookup: { from: "users", localField: "_id", foreignField: "_id", as: "customer" } },
// 5. Şekillendir (SELECT)
{ $project: { name: { $arrayElemAt: ["$customer.name", 0] }, totalAmount: 1 } }
])
Bu pipeline, C++ seviyesinde optimize edilmiştir. Raporlama ve analitik için SQL’i aratmaz.
5. ACID Transactions: Gerekli mi?
MongoDB 4.0 ile Multi-Document ACID Transactions desteği geldi. Yani birden fazla dökümanı atomik olarak güncelleyebilirsiniz. “Harika! Artık SQL gibi kullanabilirim!” HAYIR. Transaction, performans maliyeti getirir (Locking). Eğer veri modeliniz doğruysa (Embedding), zaten tek bir dökümanı güncelliyorsunuzdur. MongoDB’de tek döküman (Single Document) işlemleri her zaman atomiktir. Transaction’ı sadece, gerçekten mecbur kaldığınızda (örn: Banka havalesi, A hesabından düş B hesabına ekle) kullanın. Her güncelleme için Transaction açıyorsanız, veri modeliniz yanlıştır.
6. Python ODM: Beanie ile Modern Kullanım
Python dinamik bir dil olduğu için, veritabanından gelen verinin “neye benzediğini” bilmek zordur. PyMongo size ham dict döner. Bu da KeyError riskini artırır. Modern projelerde Beanie (Asenkron) gibi, Pydantic tabanlı ODM’ler kullanın.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from beanie import Document, init_beanie
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Category(BaseModel):
name: str
class Product(Document):
name: str
price: float
category: Category # Embedded Document
class Settings:
name = "products"
# Kullanım
tv = Product(name="OLED TV", price=50000, category=Category(name="Electronics"))
await tv.insert()
Bu sayede kodunuz tip güvenli (Type Safe) olur ve IDE’niz size otomatik tamamlama sunar.
7. Sharding: Büyümenin Bedeli
Veriniz tek bir sunucuya (örneğin 2TB disk) sığmadığında ne yapacaksınız? SQL dünyasında bu büyük bir sorundur (Vertical Scaling - Daha pahalı sunucu al). MongoDB’de ise Sharding (Horizontal Scaling) vardır. Veriyi parçalayıp farklı sunuculara dağıtır. Ancak Sharding, operasyonel yükü çok artırır. Shard Key (Parçalama Anahtarı) seçimi hayati önem taşır. Eğer yanlış anahtar seçerseniz (örn: monoton artan date), tüm yük tek bir sunucuya biner (Hotspot) ve diğer sunucular yatar. Kural: Veri boyutunuz 4TB’ı geçmeden Sharding yapmayın. Replica Set çoğu zaman yeterlidir.
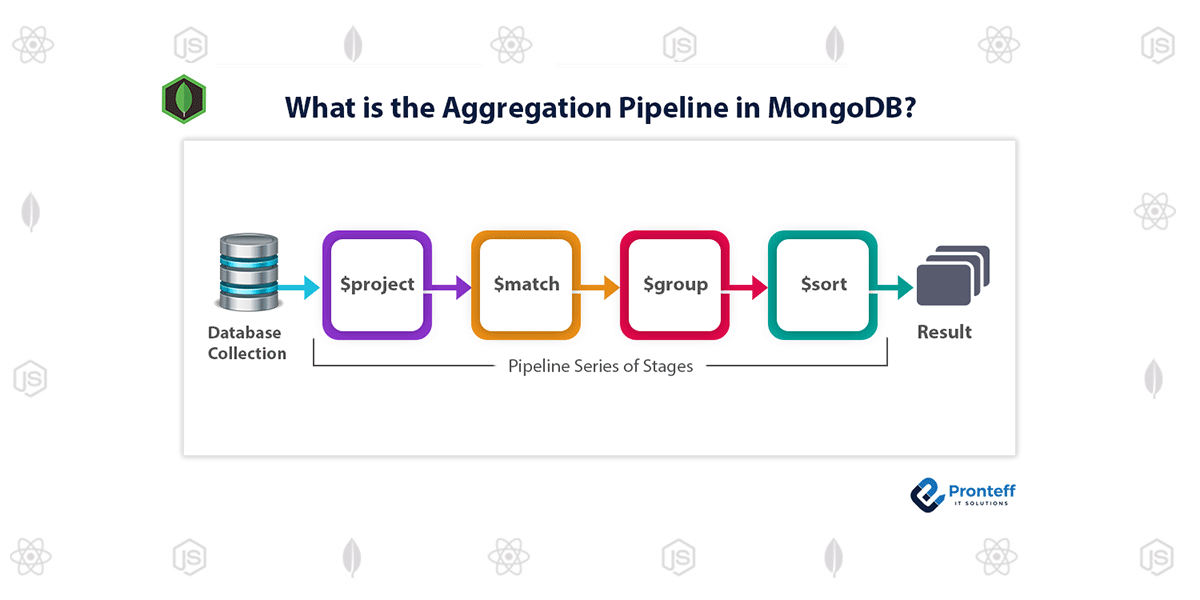 Match -> Group -> Project ile veriyi işleme akışı.
Match -> Group -> Project ile veriyi işleme akışı.
Sonuç
MongoDB, gelişi güzel veri atılacak bir JSON deposu değildir. Veri erişim desenlerinize (Access Patterns) göre çok sıkı bir tasarım süreci gerektirir. İlişkisel veritabanlarında “Veriyi normalleştir, sonra dilediğin gibi sorgula” mantığı vardır (Write Optimized). MongoDB’de ise “Nasıl sorgulayacağını bil, ona göre modelle” mantığı vardır (Read Optimized). Sorgularınızı önceden bilmeden şema tasarlamak, MongoDB’de performans sorunlarının ana kaynağıdır. Eğer veriniz hiyerarşik ise, şemanız sık değişiyorsa ve Sharding ile yatay ölçeklenme (Scale-Out) ihtiyacınız varsa MongoDB doğru tercihtir. Doğru işe doğru araç ilkesini unutmayın; bazen en iyi NoSQL veritabanı, iyi yapılandırılmış bir PostgreSQL’dir.