Python'da Asenkron Görevler: Celery vs Arq
Uzun süren işlemleri kullanıcıya bekletmeyin. Celery'nin ağırlığından kurtulup Arq ve Redis ile modern, hafif bir kuyruk sistemi kurun.
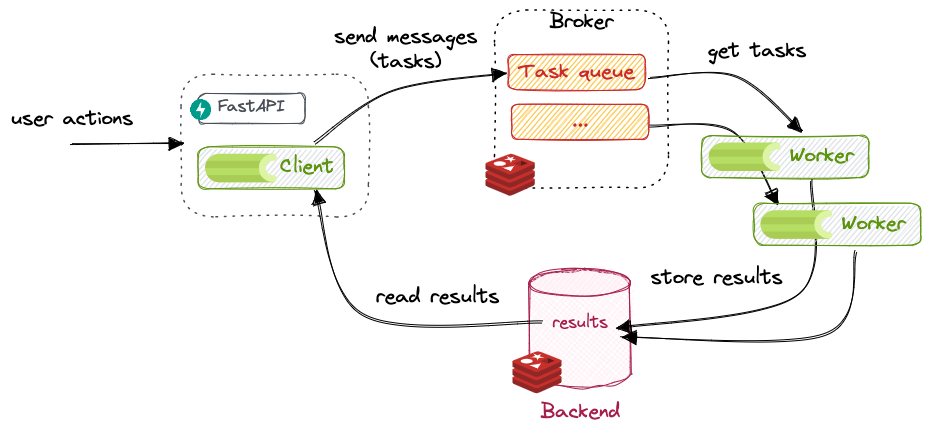
Bir web uygulamasında “Kayıt Ol” butonuna basıldığında, kullanıcının e-postasına “Hoş Geldin” maili gitmesi 3 saniye sürüyorsa, o 3 saniye kullanıcı için bir ömürdür. Daha kötüsü, eğer mail sunucusu o an yanıt vermezse, kullanıcının kaydı da başarısız olur. Bu kabul edilemez.
Çözüm 20 yıldır değişmedi: Asenkron Görev Kuyrukları (Task Queues). HTTP isteğini (Request) minimum sürede bitirip, ağır işleri (Mail atma, Raporlama, Video işleme) arkadaki işçilere (Worker) devretmek.
Python dünyasında yıllardır standart Celery idi. Ancak modern (Asyncio) dünyada yeni bir oyuncu var: Arq. Bu yazıda, production tecrübelerime dayanarak, devasa Celery konfigürasyonlarıyla boğuşmak yerine ne zaman Arq kullanmanız gerektiğini ve dağıtık sistemlerin kronik sorunlarını (Idempotency, Visibility Timeout) inceleyeceğiz.
1. Celery: İsviçre Çakısı mı, İsviçre Ordusu mu?
Celery, Django döneminin tartışmasız kralıdır. RabbitMQ, Redis, SQS, Kafka… Her şeyi destekler. Canvas, Chord, Chain, Group gibi çok gelişmiş iş akışı (workflow) özellikleri vardır.
Ama bedeli ağırdır. Basit bir “Mail At” görevi için bile:
- Broker (RabbitMQ) gerekir.
- Result Backend (Redis/Postgres) gerekir.
- Worker processleri (çok RAM yer) gerekir.
- Beat (zamanlanmış görevler) ayrı çalışır.
1
2
3
4
5
# Celery Config Complexity
app = Celery('tasks', broker='pyamqp://guest@localhost//')
app.conf.task_acks_late = True # İş bitmeden onaylama
app.conf.worker_prefetch_multiplier = 1 # RabbitMQ'yu boğma
app.conf.task_reject_on_worker_lost = True
Bu ayarları yapmazsanız, worker öldüğünde görevleriniz kaybolur (Data Loss). Celery varsayılan ayarları “Güvenlik” değil “Hız” odaklıdır. Bu bir tuzaktır.
2. Arq: Hızlı, Hafif ve Modern
Arq, asyncio ve redis üzerine kuruludur. Worker’lar Thread veya Process değil, Coroutine kullanır. Yani tek bir process’te 50MB RAM ile binlerce I/O bound işi (HTTP request, DB query) aynı anda yapabilir. Celery’de bunu yapmak için Gevent veya Eventlet ile takla atmanız gerekir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
import asyncio
from arq import create_pool
from arq.connections import RedisSettings
# Görevi Kuyruğa At (Producer)
async def main():
redis = await create_pool(RedisSettings())
# job_id=None derseniz otomatik UUID atanır.
# Ancak Idempotency için job_id'yi kendiniz verin!
await redis.enqueue_job('send_email', email='[email protected]', _job_id="user_123_welcome")
# Worker Tanımı
async def send_email(ctx, email):
# Async kütüphaneler (aiohttp, asyncpg) burada doğal olarak çalışır
await aiohttp_client.post(..., json={'email': email})
class WorkerSettings:
functions = [send_email]
on_startup = startup
on_shutdown = shutdown
3. Dağıtık Sistem Tuzakları (Distributed Pitfalls)
Kuyruk sistemi kuruyorsanız şu terimleri bilmek zorundasınız:
A. Idempotency (Tekrarlanabilirlik)
Network hatası oldu, ACK gitmedi. RabbitMQ aynı görevi tekrar worker’a gönderdi. Kullanıcıya 2 kere “Hoş Geldin” maili mi gidecek? Ya da kullanıcının bakiyesinden 2 kere para mı düşecek? Göreviniz Idempotent olmalı. Yani 1 kere de çalışsa, 10 kere de çalışsa sonuç aynı olmalı. Çözüm: Görev içinde “Bu iş yapıldı mı?” kontrolü yapın veya _job_id parametresini uniq verin (Arq, aynı ID’li iş aktifse ikincisini reddeder).
B. Visibility Timeout (Görünmezlik Süresi)
Worker işi aldı, işlemeye başladı ama 5 dakika sürdü. Broker (Redis/SQS) diyor ki: “Bu worker 1 dakikadır ses vermiyor, sanırım öldü.” Görevi başka bir worker’a daha verir. Sonuç: Aynı anda çalışan iki worker, Race Condition. Çözüm: İşinizin maksimum süresini bilin ve Timeout ayarını ona göre yapın.
C. Transactional Integrity
Kullanıcıyı DB’ye kaydettiniz, sonra kuyruğa iş attınız. Ya DB commit başarısız olursa? Kuyrukta “olmayan kullanıcı” için iş oluşur. Çözüm: Commit on Success pattern. Kuyruğa iş atma eylemini, transaction başarıyla bittikten sonraya saklayın. Django’da transaction.on_commit hook’u bunun içindir.
4. Broker Savaşı: RabbitMQ vs Redis
Celery İçin:
- RabbitMQ: Kesinlikle önerilir. Mesaj garantisi (ACK mechanism) çok sağlamdır. Routing (Topic, Fanout) yetenekleri vardır.
- Redis: Hızlıdır ama RAM’de tutar. Redis çökerse Persistence ayarı yoksa görevler uçar. Ayrıca Visibility Timeout yönetimi RabbitMQ kadar hassas değildir.
Arq İçin:
- Sadece Redis destekler. Ancak Redis Streams veya List yapılarını çok akıllıca kullanır. Basit ve orta ölçekli işler için (özellikle I/O bound) yeterince güvenilirdir.
5. İzleme (Monitoring)
Celery için standart Flower‘dır. Görsel olarak işleri, worker durumlarını gösterir. Arq için de dashboardlar var (arq-dashboard) ama ben genelde Prometheus exporter yazıp Grafana’dan izlemeyi tercih ediyorum.
İzlemeniz gereken 3 metrik:
- Queue Depth: Sırada bekleyen kaç iş var? (Artıyorsa worker yetmiyor).
- Latency: Bir iş kuyruğa girdikten ne kadar süre sonra çalışmaya başladı?
- Failure Rate: Fail olan işlerin oranı.
6. Hangisini Seçmeli?
Celery Seçin Eğer:
- Enterprise seviyesinde güvenilirlik (RabbitMQ) lazımsa.
- Karmaşık iş akışları (Workflow: A bitsin B başlasın, C paralel koşsun) varsa.
- Legacy (Sync) bir projeniz varsa.
Arq Seçin Eğer:
- Modern, Asyncio tabanlı (FastAPI/Starlette) bir projeniz varsa.
- Redis zaten stack’inizde varsa.
- Mikroservisleriniz küçük ve hızlı olsun istiyorsanız.
- Binlerce I/O işlemini az kaynakla yapmak istiyorsanız.
7. Production Checklist: Canlıya Çıkmadan Önce
Celery veya Arq fark etmez, şu maddeleri kontrol etmeden deploy almayın:
Always Set Timeouts (Soft vs Hard): İşlem sonsuz döngüye girerse worker kilitlenir.
soft_time_limit: İşleme “Lütfen dur” sinyali (SIGUSR1) gönderir.time_limit: İşlemi zorla öldürür (SIGKILL). Arq içinde:@job(timeout=60)Heartbeat Ayarları: Network dalgalanmasında worker’ın sistemden düşmemesi için Heartbeat ayarını artırın. Varsayılan genelde çok düşüktür.
Result Backend Expiration: İş sonuçlarını (return values) sonsuza kadar saklamayın. Redis’i çöplüğe çevirirsiniz.
result_expires=3600(1 saat) iyidir.Prefetch Multiplier: Uzun süren işleriniz varsa (örn: Video işleme), bu değeri
1yapın. Yoksa hızlı worker boş otururken, yavaş worker’ın üzerinde 10 tane iş birikir (Starvation). Kısa işler (Mail atma) için4veya8olabilir.Deduplication: RabbitMQ’da aynı mesajın iki kere gelme ihtimali milyonda birdir ama vardır. Kodunuzun “Bu iş zaten yapıldı mı?” kontrolü (Idempotency) hayat kurtarır.
8. Bonus: Circular Import Cehennemi ve Çözümü
Celery’e yeni başlayanların %90’ı ImportError alır. tasks.py, models.py‘ı import eder. models.py, tasks.py‘ı import eder (çünkü model save olunca task tetiklenir). Sonuç: Döngüsel Import Hatası.
Çözüm:
- Lazy Import: Taskları fonksiyon içinde import edin.
- Sinyaller: Django Signals veya SQLAlchemy Events kullanarak business logic ile task logic’i ayırın.
- Dedicated Module:
proj/tasks/paketi oluşturun ve modüllere bölün (email_tasks.py,report_tasks.py).
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Kötü Örnek (Circular Import yapar)
from myapp.models import User
@app.task
def process_user(user_id):
user = User.objects.get(id=user_id)
1
2
3
4
5
6
# İyi Örnek (Best Practice)
@app.task
def process_user(user_id):
# Model importunu fonksiyon içine al (Lazy Import)
from myapp.models import User
user = User.objects.get(id=user_id)
Bu küçük detay, saatlerce hata aramanızı engeller.
Sonuç
Asenkron kuyruklar, ölçeklenebilir sistemlerin kalbidir. Ancak “Arkaya attım, bitti” derseniz yanılırsınız. Idempotency, Error Handling (Retry) ve Monitoring kurgusunu yapmazsanız, o kuyruk bir gün patlar ve binlerce siparişi/maili kaybedersiniz. Basit başlayın (Arq), ihtiyaç duyarsanız karmaşığa (Celery) geçin. Ama her zaman Idempotent kod yazın.