Web3 ile DEX Aggregator Geliştirme: En İyi Fiyatı Bulmak
Uniswap, SushiSwap ve diğer DEX'leri tarayarak en iyi fiatı bulan, gas optimizasyonu yapan ve akıllı routing mekanizması kuran kapsamlı DEX Aggregator rehberi.
Giriş: Likidite Okyanusunda Rotayı Bulmak
Merkeziyetsiz borsalar (DEX’ler) finansal özgürlüğün kapısını araladı, ancak bir sorunu da beraberinde getirdi: Likidite Parçalanması. Aynı token, Uniswap’ta farklı, SushiSwap’ta farklı fiyattan işlem görebiliyor. İşte bu noktada DEX Aggregator’lar devreye giriyor.
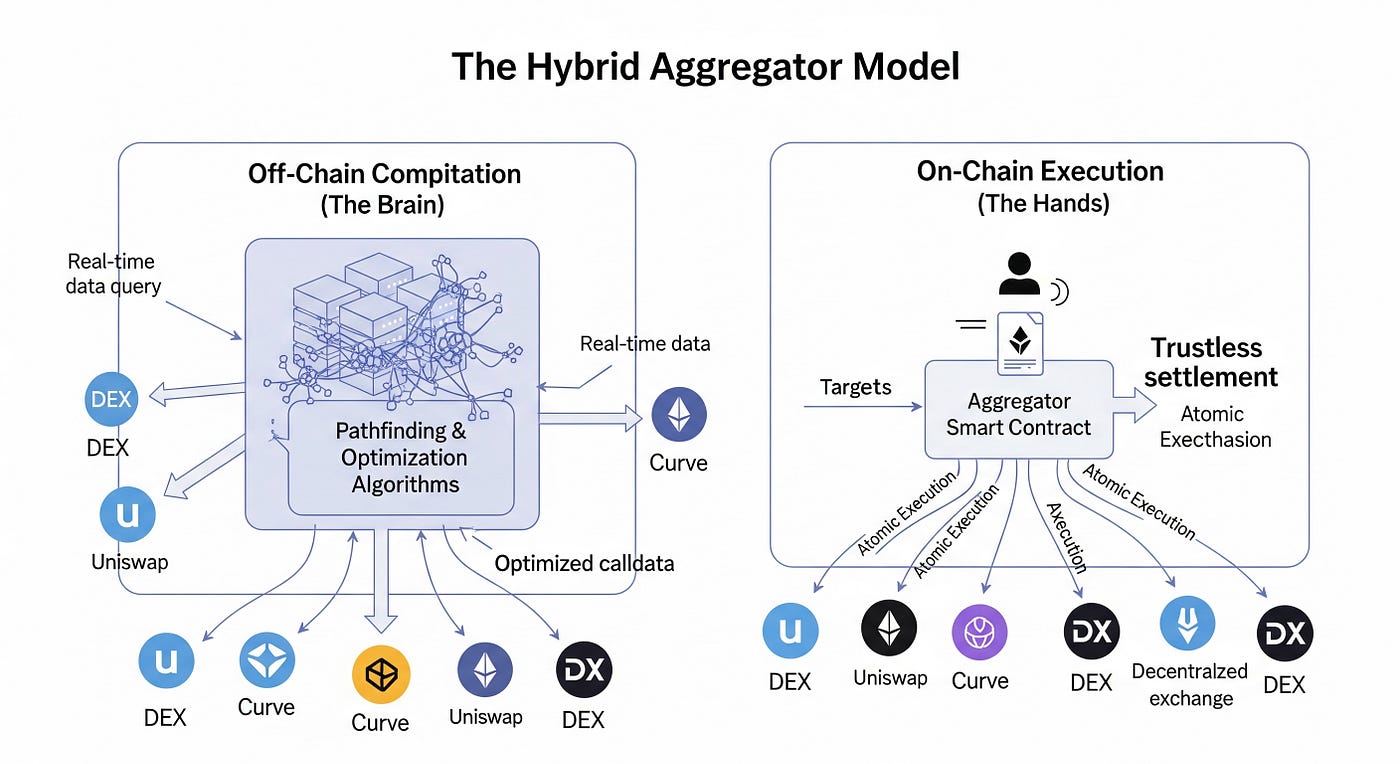
Bir “Senior Backend Engineer” gözüyle bakıldığında, bir DEX aggregator sadece fiyat soran bir bot değildir; asenkron çalışan, milisaniyelerle yarışan ve gas mâliyetlerini hesaba katarak en optimal rotayı (Smart Order Routing) çizen kompleks bir dağıtık sistemdir.
Bu rehberde, 1inch veya ParaSwap benzeri profesyonel bir aggregator’ın mimarisini, fiyat toplama mekanizmalarını ve akıllı kontrat entegrasyonunu sıfırdan inşa edeceğiz.
Fiyat Toplama Motoru (Price Discovery Engine)
Aggregator’ın kalbi, farklı kaynaklardan (Liquidity Sources) anlık fiyat verisi çeken motordur. Blokzincir verisi yavaştır; bu yüzden ethers.js veya web3.py kullanırken paralel istekler (Example: Promise.all veya asyncio.gather) kullanmak zorundasınız.
On-Chain vs Off-Chain Fiyatlama
Basit bir MVP için doğrudan akıllı kontratlardan (getAmountsOut) veri çekebilirsiniz. Ancak profesyonel bir sistemde, her blokta (12 sn) güncellenen bir Indexer servisi kullanmalısınız. Aksi takdirde, kullanıcıya gösterdiğiniz fiyat ile işlem anındaki fiyat arasında “Slippage” oluşur ve işlem başarısız olur.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// Çoklu DEX Fiyat Sorgulama (Parallel Execution)
async function getBestQuote(tokenIn, tokenOut, amount) {
const sources = [uniswap, sushiswap, pancakeswap];
// Tüm kaynaklara aynı anda soruyoruz
const quotes = await Promise.all(
sources.map(dex => dex.getQuote(tokenIn, tokenOut, amount))
);
// En yüksek çıktıyı vereni ve en düşük gas yakanı hesaplıyoruz
return optimizeRoute(quotes);
}
Smart Order Routing (SOR) Algoritması
Sadece en ucuz DEX’i bulmak yetmez. Bazen en iyi yol, paranızı bölmektir (Split Routing). Örneğin, 100 ETH bozduracaksanız; %60’ını Uniswap V3’e, %40’ını Curve havuzuna göndermek, tek bir havuza yüklenmekten çok daha az Price Impact yaratır.
Akıllı Kontrat Mimarisi: Proxy Pattern
Aggregator kontratınız, kullanıcının varlıklarını geçici olarak tutan bir “Proxy” gibi davranmalıdır. Kullanıcı parayı kontrata approve eder, kontrat işlemi yapar ve çıktıyı kullanıcıya gönderir.
Güvenlik Kritik: Kontratınızda asla bakiye tutmamalısınız. Her işlem “atomik” olmalı; yani tek transaksiyon içinde token alınmalı, swap yapılmalı ve kullanıcıya geri gönderilmelidir. Aksi takdirde, kontratta kalan “toz” (dust) bakiyeler botlar tarafından çalınabilir.
function swap(
address tokenIn,
address tokenOut,
uint256 amountIn,
uint256 minAmountOut,
Route[] calldata routes
) external payable nonReentrant {
// 1. Token'ı kullanıcıdan al
IERC20(tokenIn).transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), amountIn);
// 2. Rotaları takip et ve swap yap
for (uint i = 0; i < routes.length; i++) {
_executeSwap(routes[i]);
}
// 3. Çıktıyı kullanıcıya gönder
uint256 balance = IERC20(tokenOut).balanceOf(address(this));
require(balance >= minAmountOut, "High Slippage");
IERC20(tokenOut).transfer(msg.sender, balance);
}
Gas Optimizasyonu: Call Data Compression
Ethereum’da her byte veri gas demektir. Özellikle Layer 2 çözümlerinde (Arbitrum, Optimism) “calldata” maliyeti işlem maliyetinin büyük kısmını oluşturur.
Profesyonel bir aggregator, swap verilerini (adresler, miktarlar) sıkıştırarak gönderir. Örneğin, 20 byte’lık token adresini tam göndermek yerine, kontrat içinde önceden tanımlanmış bir “ID” (uint8) ile eşleştirmek %90’a varan gas tasarrufu sağlayabilir.
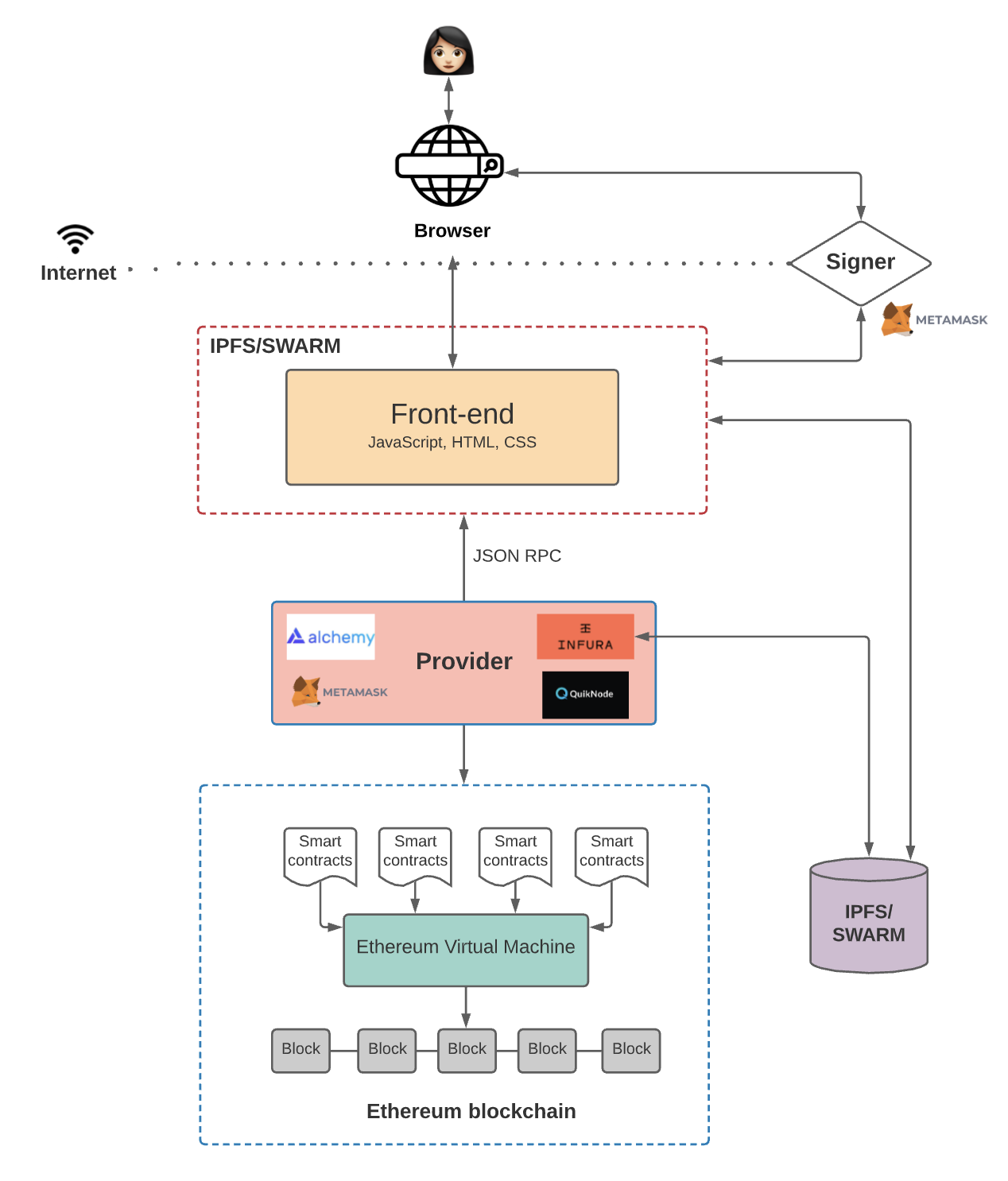
Backend API: Hızın Kaynağı
Birçok eğitim videosunda routing işleminin frontend (React/Next.js) tarafında yapıldığı gösterilir. Ancak bu yanlıştır. Tarayıcıda milyonlarca olası yolu hesaplamak cihazı kilitler. Bu ağır işlem (computation heavy) Node.js veya Rust ile yazılmış güçlü bir backend servisinde yapılmalıdır.
Neden Backend Şart?
- Gizli API Anahtarları: Infura/Alchemy keylerinizi frontend’de ifşa etmezsiniz.
- Önbellekleme (Caching): Popüler çiftler (ETH/USDC) için rotayı her seferinde hesaplamak yerine, Redis’te 5 saniye cache tutabilirsiniz. Bu sayede RPC node’una giden istek sayısını %80 azaltırsınız.
- Hız Limiti (Rate Limiting): DEX API’leri genellikle IP tabanlı limitler uygular. Backend sunucunuzda bu limitleri yönetmek ve istekleri kuyruğa almak (queueing), sisteminizin çökmesini engeller.
- MEV Koruması: Kullanıcı işlemini public mempool yerine Flashbots RPC üzerinden göndererek front-running riskini minimize edebilirsiniz.
- API Dokümantasyonu: Backend servisinizin diğer geliştiriciler tarafından kullanılabilmesi için Swagger veya Redoc ile dokümante edilmesi, projenizin profesyonellik seviyesini artırır.
Slippage Protection: Kullanıcıyı Korumak
Merkeziyetsiz borsalarda fiyat anlık değişir. Kullanıcı “Swap” butonuna bastığı an ile işlemin bloğa girdiği an arasındaki fiyat farkına “Slippage” denir.
Aggregator olarak göreviniz, kullanıcıya “Minimum Receive” garantisi vermektir. Eğer kullanıcı %1 slippage kabul etmişse ve işlem sırasında fiyat %1.5 düşerse, akıllı kontratınız işlemi require(amountOut >= minAmountOut) ile iptal etmelidir (revert).
1
2
3
// Slippage Hesaplama
const slippageTolerance = 0.5 // %0.5
const minAmountOut = amountOut.mul(100 - slippageTolerance).div(100);
Multi-Hop Routing: Rota Optimizasyonu
Bazen A tokeninden B tokenine doğrudan geçiş (Direct Swap) en karlı yol olmayabilir. A -> ETH -> USDC -> B rotası, havuz derinliğine bağlı olarak daha iyi bir fiyat sunabilir. Aggregator’ınızın “Graph Theory” (Dijkstra veya Bellman-Ford algoritmaları) kullanarak en kısa ve karlı yolu bulması gerekir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// Basit Multi-Hop Mantığı
async function findBestMix(tokenIn, tokenOut) {
const direct = await getDirectPrice(tokenIn, tokenOut);
const viaETH = await getHopPrice(tokenIn, "ETH", tokenOut);
const viaUSDC = await getHopPrice(tokenIn, "USDC", tokenOut);
return Math.max(direct, viaETH, viaUSDC);
}
Bu basit matematik, kullanıcılarınızın binlerce dolar zarar etmesini engeller.
Frontend: Web3 React ile Bağlantı
Kullanıcı arayüzü, arka plandaki tüm bu karmaşıklığı gizlemelidir. web3-react veya wagmi kütüphanelerini kullanarak cüzdan bağlantısını yönetebilirsiniz. Ancak en önemli kısım User Feedback‘tir.
İşlem beklemedeyken (pending) dönen bir spinner, işlem onaylandığında çıkan bir konfeti ve hata durumunda (örn: “Insufficient Balance”) çıkan açıklayıcı bir toast mesajı, iyi bir dApp’i amatör olandan ayırır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// Web3-React Hook Kullanımı
const { activate, library } = useWeb3React();
const connectWallet = async () => {
try {
await activate(injected);
console.log("Cüzdan bağlandı!");
} catch (ex) {
console.error("Bağlantı hatası:", ex);
}
};
Production Monitoring: Grafana ve Prometheus
Canlıya aldığınız aggregator’ın sağlığını izlemek hayati önem taşır. Hangi RPC node’u yavaş yanıt veriyor? En çok hangi token çiftleri işlem görüyor? Slippage yüzünden iptal olan işlem oranı ne?
Bu metrikleri Prometheus ile toplayıp Grafana dashboard’larında görselleştirmek, performans darboğazlarını (bottlenecks) erkenden tespit etmenizi sağlar.
Teknik Sözlük (Glossary)
- Dex Aggregator: Birden fazla borsayı tarayarak en iyi fiyatı sunan platform (Örn: 1inch).
- Slippage: Beklenen fiyat ile gerçekleşen fiyat arasındaki fark.
- Price Impact: İşleminizin büyüklüğünün havuzdaki fiyatı ne kadar değiştirdiği.
- Smart Order Routing (SOR): Bir işlemi parçalayarak birden fazla havuza dağıtan algoritma.
- Gas Optimization: İşlem maliyetini düşürmek için yapılan kod iyileştirmeleri.
- Calldata: Ethereum işlemlerinde veri taşıyan, depolamadan daha ucuz olan alan.
- Indexer: Blokzincir verilerini okuyup hızlı sorgulanabilir veritabanlarına kaydeden servis (Örn: The Graph).
Sonuç: DeFi’nin Geleceği Aggregation
Likidite parçalanmaya devam ettikçe, Aggregator’ların önemi artacaktır. Bir geliştirici olarak sadece fiyat bulan değil, rotayı optimize eden ve güvenliği ön planda tutan sistemler kurmalısınız.
Bu altyapıyı daha da ileri götürmek isterseniz, Flash Loan Arbitraj Botu ile bu fiyat farklarından kar elde etmeyi öğrenebilir veya Smart Contract Güvenlik Pratikleri ile kontratınızı saldırılara karşı koruyabilirsiniz.
Sorularınız ve kod incelemeleri için aşağıdaki yorum bölümünü kullanmaktan çekinmeyin, topluluğun gücüyle her zaman daha iyi kod yazarız.