Python ile Otomatik Yatırım (Trade) Sistemleri Geliştirmek
Python ile uçtan uca otomatik yatırım sistemleri geliştirme rehberi. Mimari tasarım, backtesting, risk yönetimi ve canlı ortam deployment stratejileri.
Giriş: Algoritmik Ticaretin Evrimi ve Mühendislik Disiplini
Finansal piyasalar, artık sadece ekonomik verilerin değil, milisaniyelerle yarışan algoritmaların hüküm sürdüğü bir savaş alanı. Bir senior yazılım mühendisi için bir trading botu geliştirmek, sadece “al/sat” sinyali üreten bir script yazmak değildir; bu, yüksek erişilebilirlik, düşük gecikme (latency) ve hataya yer bırakmayan bir risk yönetimi mekanizması kurma sürecidir.
İnsan duygu ve hatalarından arındırılmış, 7/24 piyasayı tarayan ve saniyeler içinde binlerce işlem yürütebilen bu sistemlerin kalbinde bugün genellikle Python yer alıyor. Geniş kütüphane desteği (Pandas, NumPy, CCXT) ve hızlı prototipleme imkanı, Python’ı kantitatif analizlerin vazgeçilmezi kılıyor. Ancak, profesyonel bir sistemde “çalışan kod” yeterli değildir; sistemin sürdürülebilir, test edilebilir ve her şeyden önemlisi “güvenli” olması gerekir. Bu yazıda, basit bir script’ten profesyonel bir trading mimarisine giden yolu inceleyeceğiz.
Sistem Mimarisi: Modüler Bir Yapı Kurmak
Profesyonel bir yatırım sistemi, birbirine sıkı sıkıya bağlı olmayan (loosely coupled) modüllerden oluşmalıdır. Bu sistemin “spagetti” koda dönüşmesini engeller ve modüllerin bağımsız olarak test edilmesini sağlar.
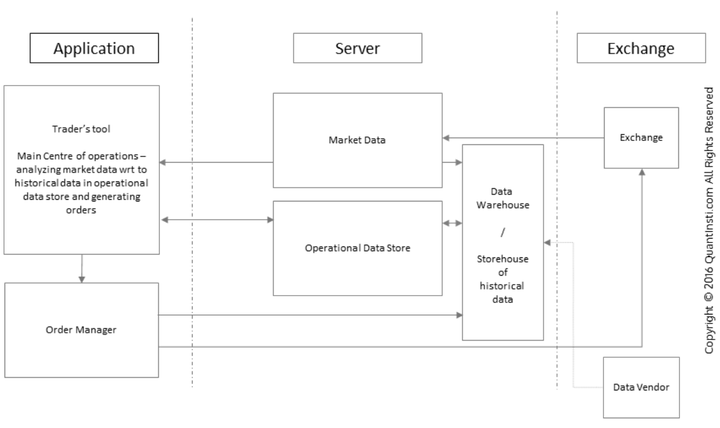
1. Veri Katmanı (Data Layer)
Sistemin can damarı market verisidir. REST API’lar geçmiş veriler için uygun olsa da, canlı ortamda düşük gecikme için WebSocket kullanımı şarttır. Senior bir yaklaşımda, veri çekme işlemi ana business logic’ten izole edilir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
import ccxt
import pandas as pd
class MarketData:
def __init__(self, exchange_id='binance'):
self.exchange = getattr(ccxt, exchange_id)({
'enableRateLimit': True,
'options': {'defaultType': 'future'}
})
def get_ohlcv(self, symbol, timeframe='1h', limit=100):
# REST ile geçmiş veri çekme
ohlcv = self.exchange.fetch_ohlcv(symbol, timeframe, limit=limit)
df = pd.DataFrame(ohlcv, columns=['time', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close', 'vol'])
df['time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['time'], unit='ms')
return df
2. Strateji Motoru (Strategy Engine)
Burası “beyin” kısmıdır. Sadece teknik analiz indikatörleri değil, aynı zamanda kompleks matematiksel modeller veya yapay zeka algoritmaları burada koşar. Stratejiler genellikle bir BaseStrategy sınıfından kalıtım alarak standartlaştırılmalıdır.
Senior Notu: Basit hareketli ortalama (Moving Average) kesişimleri lab ortamında güzel görünse de, canlı piyasada kayma (slippage) ve komisyonlar nedeniyle genellikle yanıltıcıdır. Profesyonel sistemlerde daha çok istatistiksel arbitraj (Stat Arb) veya duygu analizi (Sentiment Analysis) gibi daha sofistike yöntemler tercih edilir.
3. Emisyon ve Yürütme Katmanı (Execution Layer)
Stratejiden gelen sinyalleri gerçek emir dosyalarına dönüştüren katmandır. Burada sadece “market order” değil, gelişmiş emir tipleri (Limit, Iceberg, Fill-or-Kill) yönetilmelidir. Ayrıca, emirlerin gerçekleşme durumunu takip eden bir “Order Tracker” mekanizması elzemdir.
4. Risk Yönetimi (Risk Management) - Olmazsa Olmaz
Bir botu batıracak olan stratejisi değil, hatalı risk yönetimidir. Senior seviyesindeki bir sistemde risk yönetimi stratejiden bağımsız bir “onay mekanizması” gibi çalışır.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class RiskControl:
def __init__(self, max_risk_per_trade=0.02, total_stop_loss=0.1):
self.max_risk = max_risk_per_trade
self.global_stop = total_stop_loss
def validate_order(self, order_size, balance):
# Toplam bakiyenin %2'sinden fazla risk alınıyor mu?
if order_size > balance * self.max_risk:
return False, "Risk limit exceeded"
return True, "Valid"
Strateji Geliştirme: Akademik Modelden Canlı Piyasaya
Bir trading botu geliştirirken en büyük yanılgı, aşırı optimizasyon (overfitting) tuzağına düşmektir. Geliştirilen modelin sadece geçmiş verilerde değil, farklı piyasa koşullarında da dirençli (robust) olması gerekir.
İndikatörlerden Öte: Makine Öğrenmesi
Günümüzde senior mühendisler, teknik indikatörlerin ötesine geçerek XGBoost, LSTM veya Reinforcement Learning gibi modelleri trading sistemlerine entegre ediyorlar. Ancak bu modellerin “siyah kutu” (black box) olması, risk yönetimini daha da kritik hale getiriyor.
Sinyal Doğrulama ve Slippage
Canlı piyasada emir gönderdiğiniz fiyat ile emrin gerçekleştiği fiyat arasında fark oluşur (Slippage). Bu fark, yüksek frekanslı (HFT) işlemlerde kar marjını tamamen eritebilir. Bu yüzden, trading motorunuzda her zaman bir “slippage buffer” hesabı yapmalısınız. Ayrıca, büyük emirlerin piyasayı etkilememesi için parçalı emir (TWAP/VWAP) stratejileri uygulanmalıdır.
Backtesting: Geçmişin Tuzakları
“Backtest”, bir stratejinin geçmiş verilerdeki performansını ölçmektir. Ancak birçok junior geliştirici burada ölümcül hatalar yapar. Bir senior mühendis olarak backtest yaparken şu üç noktaya odaklanırım:
- Look-ahead Bias: Kodunuzda henüz gerçekleşmemiş bir veriye erişme hatasıdır. Örneğin, bugünkü kapanış fiyatına bakarak dünkü emri gerçekleştirmek gibi.
- Survivorship Bias: Sadece hala piyasada olan (hayatta kalan) varlıkları test etmek. İflas edenleri göz ardı etmek başarı oranını yapay olarak şişirir.
- İşlem Maliyetleri: Komisyonları, funding fee’leri ve bid-ask spread’i hesaba katmayan her backtest sadece bir fantezidir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def backtest(data, strategy, initial_balance=10000):
balance = initial_balance
commission = 0.0004 # %0.04 Binance komisyonu
for i in range(len(data)):
signal = strategy.get_signal(data[:i])
if signal == 'BUY':
# Komisyonu ve slippage payını düşmeyi unutmayın!
balance -= (data['close'][i] * commission)
# ... işlem mantığı
Canlı Yayında İzleme ve Log Yönetimi
Bir trading botu canlıya çıktığında, o artık bir finansal operasyondur. Sistemin anlık sağlık durumunu izlemek için “Observability” prensiplerini uygulamalıyız.
- Centralized Logging: Tüm işlemler, hatalar ve sinyaller merkezi bir yerde (Logstash, Grafana) toplanmalıdır.
- Alerting: Beklenmedik bir hata (API bağlantı kaybı, bakiye uyarısı) durumunda anlık bildirim (Telegram/Slack) mekanizması devrede olmalıdır.
- Circuit Breakers: Eğer sistem üst üste belirli sayıda hata alıyorsa veya bakiye belirli bir oranın altına düştüyse bot kendini otomatik olarak kapatmalıdır (Self-preservation).
Mühendislik Tavsiyesi: Botunuzu asla ana bilgisayarınızda çalıştırmayın. Düşük gecikmeli, güvenilir bir cloud provider (AWS, DigitalOcean) üzerinden ve tercihen Docker ile Python Uygulaması Containerization rehberimizde anlattığımız gibi konteynerize edilmiş bir yapıda koşturun.
İleri Seviye Stratejiler ve Yaklaşımlar
Basit indikatörlerin ötesine geçtiğimizde, piyasada “alfa” yaratmak için daha sofistike yöntemler devreye girer.
1. İstatistiksel Arbitraj (Stat-Arb)
Aralarında yüksek korelasyon olan iki varlığın (örneğin BTC ve ETH) fiyat farkındaki geçici sapmalardan kar etmeyi hedefler. Fiyatlar ortalamaya (mean reversion) döndüğünde kar realize edilir.
2. Market Making (Piyasa Yapıcılık)
Sürekli olarak alış ve satış yönünde emir girerek spread farkından (bid-ask spread) kazanç sağlamayı amaçlar. Burada en büyük risk, piyasanın hızla tek yöne gitmesidir (inventory risk).
3. Sentiment Analysis (Duygu Analizi)
X (Twitter), Reddit veya haber sitelerindeki verileri NLP (Doğal Dil İşleme) ile analiz ederek piyasa yönünü tahmin etmeye çalışır. “Elon Musk bir tweet attığında DOGE al/sat” botları bunun en popüler örneğidir. Ancak bu yaklaşımda, sahte haberleri (fake news) ve manipülatif botları ayırt edebilecek sağlam bir veri temizleme katmanı şarttır.
Emir Tipleri ve Yürütme Stratejileri
Sadece “Market” ve “Limit” emirleriyle yetinmek, profesyonel bir trader için yeterli değildir.
- Iceberg Orders: Çok büyük bir emri küçük parçalara bölerek piyasanın derinlik tablosunda (order book) fark edilmemesini sağlar.
- Post-Only: Emrin her zaman piyasa yapıcı (maker) olarak girilmesini garanti eder, böylece piyasa alıcı (taker) komisyonu ödemekten kurtulursunuz.
- Trailing Stop: Fiyat karda ilerledikçe stop seviyesini otomatik olarak yukarı (veya aşağı) çeken dinamik bir risk yönetimi aracıdır.
Deployment: Botu Evrenselleştirmek
Yazdığınız kodun her zaman her yerde aynı çalışmasını sağlamak için Docker kullanımı elzemdir.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
# API Key'leri asla kopyalamayın! Çevre değişkenlerinden alın.
CMD ["python", "bot_launcher.py"]
AWS Üzerinde Yaygın Kurulum:
- EC2: Botun ana çalışma ünitesi. Gecikme süresi (latency) için borsanın sunucularına en yakın bölgeyi (Genellikle Tokyo veya İrlanda) seçin.
- RDS: Trade geçmişi ve performans verilerini saklamak için güvenilir SQL veritabanı.
- CloudWatch: Botun RAM/CPU tüketimini ve loglarını izlemek için.
Teknik Sözlük (Glossary)
- Slippage (Kayma): Beklenen işlem fiyatı ile işlemin gerçekleştiği fiyat arasındaki fark.
- Spread: En iyi alış fiyatı ile en iyi satış fiyatı arasındaki fark.
- WebSocket: Düşük gecikmeli, iki yönlü veri trafiği sağlayan bağlantı protokolü. Piyasayı canlı izlemek için şarttır.
- Backtesting: Bir stratejinin geçmiş veriler üzerindeki performansını simüle etme süreci.
- Drawdown: Portföyün zirve noktasından ne kadar düştüğünü gösteren risk metriği.
- ATR (Average True Range): Piyasa volatilitesini ölçen bir indikatör. Risk yönetiminde stop-loss seviyesi belirlemek için sıkça kullanılır.
Son Mühendislik Notları: Psikoloji vs Matematik
Algoritmik trading, finansın soğuk dünyası ile yazılımın disiplinli dünyasının kesişimidir. Bir bot yazarken en büyük başarınız, stratejinizin ne kadar kar getirdiği değil, ne kadar “stabil” kaldığıdır. Hiçbir strateji sonsuza kadar çalışmaz; piyasa koşulları her zaman değişir (Regime Change).
Bu yüzden başarılı bir sistem; sadece iyi bir algoritmadan değil, sürekli kendini izleyen, verileri raporlayan ve en kötü senaryoda (Flash Crash) nakite geçmeyi bilen bir savunma mekanizmasından oluşur. Kendi sistemlerimden öğrendiğim en büyük ders şudur: “Matematiğe güvenin ama hatalara karşı her zaman paranoid kalın.”
Trading sistemleri geliştirmek, sabır ve sürekli öğrenme gerektiren bir yolculuktur. Python bu yolda en büyük yardımcınız, ancak disiplin en büyük rehberinizdir. Terminalden akıp giden fiyatlar arasında kendi finansal özgürlüğünüzü inşa etmek dileğiyle.
Son Bir Mühendislik Notu
Botunuzun API key’lerini yönetirken asla .env dosyalarını git ortamına push etmeyin. Secrets Manager (AWS/HashiCorp) gibi profesyonel çözümleri kullanmak, milyon dolarlık bir sızıntıyı önlemenin en temel yoludur. Güvenlik, kardan her zaman daha öncelikli gelmelidir.