Implementing ERC-20 Token Standard
Complete guide to implementing ERC-20 token standard. OpenZeppelin contracts, minting, burning, security best practices, and deployment strategies.
Introduction
The ERC-20 token standard is the most widely adopted token standard on the Ethereum blockchain, serving as the foundation for thousands of cryptocurrencies and DeFi protocols. From stablecoins like USDT and USDC to governance tokens and utility tokens, ERC-20 has become the de facto standard for fungible tokens in the blockchain ecosystem.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore every aspect of implementing an ERC-20 token, from understanding the standard’s core functions to deploying a production-ready token contract. You’ll learn about transfer mechanisms, allowances, events, security considerations, and advanced features like burning, minting, and pausability. Whether you’re building a utility token for your dApp or creating a governance token for your DAO, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools needed to create secure, efficient, and standard-compliant tokens.
 Figure 1: Smart contract architecture and execution flow
Figure 1: Smart contract architecture and execution flow
Understanding the ERC-20 Standard
What is ERC-20?
ERC-20 (Ethereum Request for Comments 20) is a technical standard used for smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain for implementing tokens. Proposed by Fabian Vogelsteller in November 2015, it defines a common list of rules that an Ethereum token must implement, giving developers the ability to program how new tokens will function within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Why ERC-20 Matters
The standardization provided by ERC-20 offers several critical benefits:
- Interoperability: All ERC-20 tokens can interact with any service that supports the standard
- Liquidity: Easy listing on exchanges that support ERC-20
- Composability: Tokens can be used across different DeFi protocols seamlessly
- Development Efficiency: Standard interface reduces development time
- Security: Well-tested standard with known security patterns
Core Functions
The ERC-20 standard mandates six essential functions and two events:
Required Functions:
totalSupply(): Returns the total token supplybalanceOf(address): Returns the balance of an accounttransfer(address, uint256): Transfers tokens to an addresstransferFrom(address, address, uint256): Transfers tokens from one address to anotherapprove(address, uint256): Approves a spender to transfer tokensallowance(address, address): Returns the remaining approved tokens
Required Events:
Transfer: Emitted when tokens are transferredApproval: Emitted when an allowance is set
Basic ERC-20 Implementation
Let’s start with a basic implementation of the ERC-20 standard in Solidity.
Simple ERC-20 Contract
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract BasicERC20 {
// Token metadata
string public name;
string public symbol;
uint8 public decimals;
uint256 public totalSupply;
// Balances mapping
mapping(address => uint256) public balanceOf;
// Allowances mapping (owner => spender => amount)
mapping(address => mapping(address => uint256)) public allowance;
// Events
event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint256 value);
event Approval(address indexed owner, address indexed spender, uint256 value);
/**
* @dev Constructor sets token details and initial supply
* @param _name Token name
* @param _symbol Token symbol
* @param _decimals Number of decimals (usually 18)
* @param _initialSupply Initial token supply
*/
constructor(
string memory _name,
string memory _symbol,
uint8 _decimals,
uint256 _initialSupply
) {
name = _name;
symbol = _symbol;
decimals = _decimals;
totalSupply = _initialSupply * 10**uint256(_decimals);
// Assign all tokens to contract creator
balanceOf[msg.sender] = totalSupply;
emit Transfer(address(0), msg.sender, totalSupply);
}
/**
* @dev Transfer tokens to a specified address
* @param _to The address to transfer to
* @param _value The amount to be transferred
* @return success True if the transfer was successful
*/
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value)
public
returns (bool success)
{
require(_to != address(0), "Cannot transfer to zero address");
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= _value, "Insufficient balance");
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= _value;
balanceOf[_to] += _value;
emit Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value);
return true;
}
/**
* @dev Approve the passed address to spend the specified amount of tokens
* @param _spender The address which will spend the funds
* @param _value The amount of tokens to be spent
* @return success True if the approval was successful
*/
function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value)
public
returns (bool success)
{
require(_spender != address(0), "Cannot approve zero address");
allowance[msg.sender][_spender] = _value;
emit Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value);
return true;
}
/**
* @dev Transfer tokens from one address to another
* @param _from address The address which you want to send tokens from
* @param _to address The address which you want to transfer to
* @param _value uint256 the amount of tokens to be transferred
* @return success True if the transfer was successful
*/
function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value)
public
returns (bool success)
{
require(_to != address(0), "Cannot transfer to zero address");
require(balanceOf[_from] >= _value, "Insufficient balance");
require(allowance[_from][msg.sender] >= _value, "Insufficient allowance");
balanceOf[_from] -= _value;
balanceOf[_to] += _value;
allowance[_from][msg.sender] -= _value;
emit Transfer(_from, _to, _value);
return true;
}
}
Understanding the Implementation
1. State Variables
name,symbol,decimals: Token metadata for identification and displaytotalSupply: Total number of tokens in existencebalanceOf: Mapping that tracks each address’s token balanceallowance: Nested mapping for approved spending limits
2. Constructor
- Initializes token metadata
- Mints initial supply to the contract deployer
- Emits Transfer event from zero address (minting convention)
3. Transfer Function
- Validates recipient address and sender balance
- Updates balances using checked arithmetic
- Emits Transfer event for tracking
4. Approve and TransferFrom
- Implements the allowance mechanism
- Enables third-party spending (crucial for DEXs and DeFi)
- Prevents double-spending attacks
Advanced ERC-20 with OpenZeppelin
OpenZeppelin provides battle-tested, secure implementations of ERC-20 with additional features.
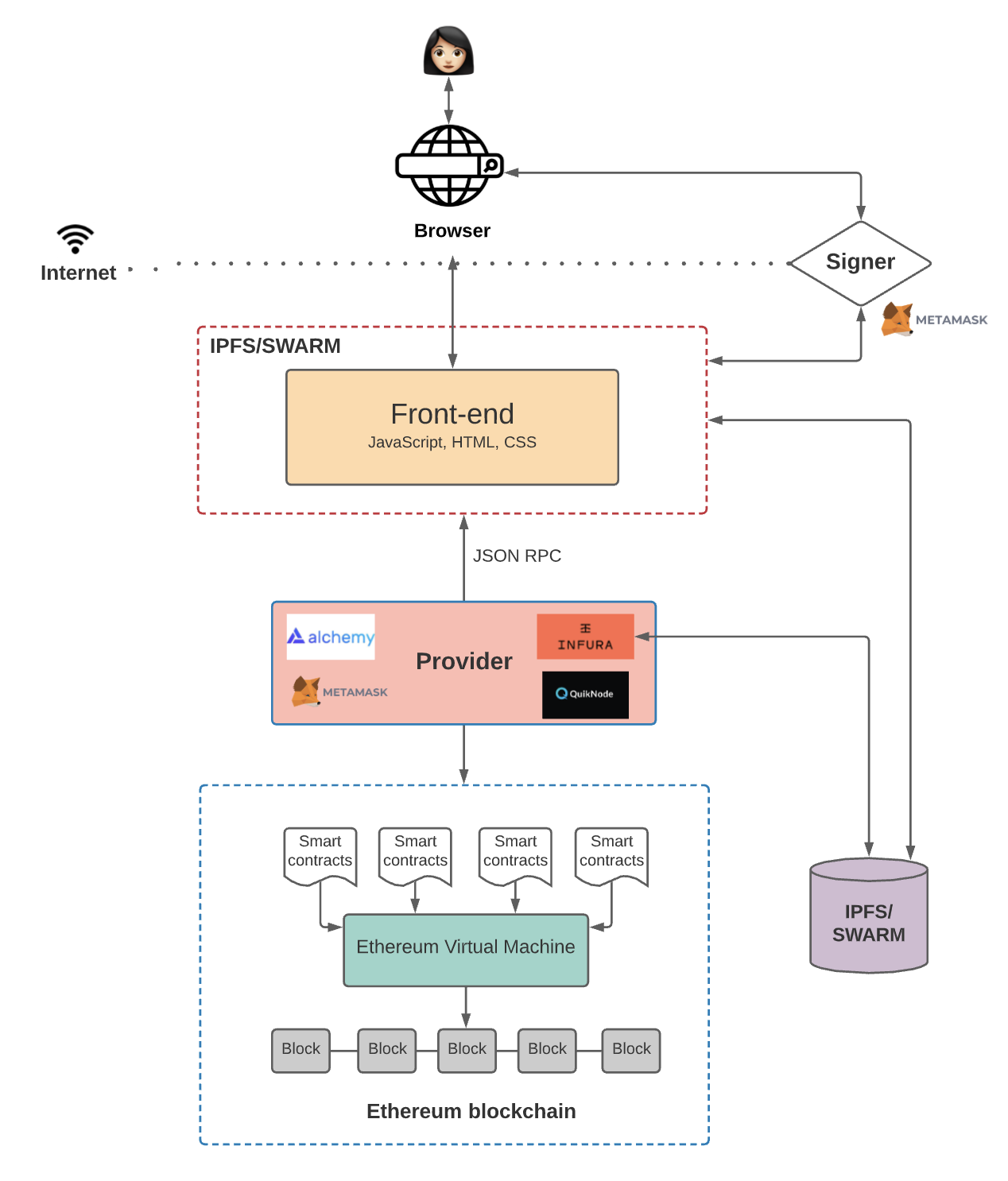 Figure 2: Web3 smart contract development architecture
Figure 2: Web3 smart contract development architecture
Installation and Setup
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Initialize npm project
npm init -y
# Install Hardhat
npm install --save-dev hardhat
# Initialize Hardhat project
npx hardhat
# Install OpenZeppelin contracts
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
# Install additional dependencies
npm install --save-dev @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-etherscan
npm install dotenv
Enhanced ERC-20 Token
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Burnable.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Pausable.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Permit.sol";
/**
* @title MyToken
* @dev Implementation of an advanced ERC20 token with additional features:
* - Minting: Owner can create new tokens
* - Burning: Token holders can destroy their tokens
* - Pausable: Owner can pause all token transfers
* - Permit: Gasless approvals using EIP-2612
* - Ownable: Access control for administrative functions
*/
contract MyToken is ERC20, ERC20Burnable, ERC20Pausable, Ownable, ERC20Permit {
// Maximum supply cap (100 million tokens)
uint256 public constant MAX_SUPPLY = 100_000_000 * 10**18;
// Minting limit per transaction (1 million tokens)
uint256 public constant MINT_LIMIT = 1_000_000 * 10**18;
// Fee structure
uint256 public transferFeePercent = 0; // 0% initially, can be 0-5%
address public feeRecipient;
// Blacklist for preventing malicious actors
mapping(address => bool) public isBlacklisted;
// Events
event FeeUpdated(uint256 newFeePercent);
event FeeRecipientUpdated(address newRecipient);
event AddressBlacklisted(address indexed account);
event AddressWhitelisted(address indexed account);
/**
* @dev Constructor sets initial token details
* @param initialOwner Address that will own the contract
*/
constructor(address initialOwner)
ERC20("MyToken", "MTK")
Ownable(initialOwner)
ERC20Permit("MyToken")
{
// Mint initial supply to contract owner
_mint(initialOwner, 10_000_000 * 10**decimals());
feeRecipient = initialOwner;
}
/**
* @dev Mint new tokens (only owner)
* @param to Address to receive minted tokens
* @param amount Amount of tokens to mint
*/
function mint(address to, uint256 amount) public onlyOwner {
require(totalSupply() + amount <= MAX_SUPPLY, "Exceeds max supply");
require(amount <= MINT_LIMIT, "Exceeds mint limit per transaction");
_mint(to, amount);
}
/**
* @dev Pause all token transfers (only owner)
*/
function pause() public onlyOwner {
_pause();
}
/**
* @dev Unpause token transfers (only owner)
*/
function unpause() public onlyOwner {
_unpause();
}
/**
* @dev Set transfer fee percentage (only owner)
* @param feePercent Fee percentage (0-500 for 0-5%)
*/
function setTransferFee(uint256 feePercent) public onlyOwner {
require(feePercent <= 500, "Fee cannot exceed 5%");
transferFeePercent = feePercent;
emit FeeUpdated(feePercent);
}
/**
* @dev Set fee recipient address (only owner)
* @param recipient Address to receive fees
*/
function setFeeRecipient(address recipient) public onlyOwner {
require(recipient != address(0), "Invalid recipient");
feeRecipient = recipient;
emit FeeRecipientUpdated(recipient);
}
/**
* @dev Blacklist an address (only owner)
* @param account Address to blacklist
*/
function blacklist(address account) public onlyOwner {
isBlacklisted[account] = true;
emit AddressBlacklisted(account);
}
/**
* @dev Remove address from blacklist (only owner)
* @param account Address to whitelist
*/
function whitelist(address account) public onlyOwner {
isBlacklisted[account] = false;
emit AddressWhitelisted(account);
}
/**
* @dev Override transfer to include fees and blacklist check
*/
function _update(address from, address to, uint256 amount)
internal
override(ERC20, ERC20Pausable)
{
require(!isBlacklisted[from], "Sender is blacklisted");
require(!isBlacklisted[to], "Recipient is blacklisted");
// Skip fee for minting/burning
if (from == address(0) || to == address(0)) {
super._update(from, to, amount);
return;
}
// Calculate and deduct fee
if (transferFeePercent > 0) {
uint256 fee = (amount * transferFeePercent) / 10000;
uint256 amountAfterFee = amount - fee;
// Transfer fee to recipient
if (fee > 0) {
super._update(from, feeRecipient, fee);
}
// Transfer remaining amount
super._update(from, to, amountAfterFee);
} else {
super._update(from, to, amount);
}
}
}
Key Features Explained
1. ERC20Burnable
- Allows token holders to destroy their tokens
- Reduces total supply permanently
- Useful for deflationary tokenomics
2. ERC20Pausable
- Emergency stop mechanism
- Pauses all token transfers
- Critical for responding to security incidents
3. ERC20Permit (EIP-2612)
- Gasless approvals using signatures
- Better UX - users don’t need ETH for approvals
- More efficient for DeFi interactions
4. Ownable
- Access control for administrative functions
- Owner can mint, pause, and manage fees
- Can transfer ownership
5. Custom Features
- Transfer fees for protocol revenue
- Blacklist functionality for compliance
- Supply cap to prevent unlimited inflation
Testing Your ERC-20 Token
Comprehensive testing is crucial for token security.
Hardhat Test Suite
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
const { expect } = require("chai");
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
describe("MyToken", function () {
let myToken;
let owner;
let addr1;
let addr2;
let addrs;
beforeEach(async function () {
// Get signers
[owner, addr1, addr2, ...addrs] = await ethers.getSigners();
// Deploy contract
const MyToken = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyToken");
myToken = await MyToken.deploy(owner.address);
await myToken.waitForDeployment();
});
describe("Deployment", function () {
it("Should set the right owner", async function () {
expect(await myToken.owner()).to.equal(owner.address);
});
it("Should assign the initial supply to the owner", async function () {
const ownerBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address);
expect(await myToken.totalSupply()).to.equal(ownerBalance);
});
it("Should have correct name and symbol", async function () {
expect(await myToken.name()).to.equal("MyToken");
expect(await myToken.symbol()).to.equal("MTK");
});
it("Should have 18 decimals", async function () {
expect(await myToken.decimals()).to.equal(18);
});
});
describe("Transactions", function () {
it("Should transfer tokens between accounts", async function () {
// Transfer 100 tokens from owner to addr1
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
const addr1Balance = await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address);
expect(addr1Balance).to.equal(ethers.parseEther("100"));
// Transfer 50 tokens from addr1 to addr2
await myToken.connect(addr1).transfer(addr2.address, ethers.parseEther("50"));
const addr2Balance = await myToken.balanceOf(addr2.address);
expect(addr2Balance).to.equal(ethers.parseEther("50"));
});
it("Should fail if sender doesn't have enough tokens", async function () {
const initialOwnerBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address);
// Try to send more tokens than available
await expect(
myToken.connect(addr1).transfer(owner.address, ethers.parseEther("1"))
).to.be.revertedWithCustomError(myToken, "ERC20InsufficientBalance");
// Owner balance shouldn't have changed
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address)).to.equal(initialOwnerBalance);
});
it("Should update balances after transfers", async function () {
const initialOwnerBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address);
// Transfer 100 tokens to addr1
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
// Transfer 50 tokens to addr2
await myToken.transfer(addr2.address, ethers.parseEther("50"));
// Check balances
const finalOwnerBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address);
expect(finalOwnerBalance).to.equal(
initialOwnerBalance - ethers.parseEther("150")
);
const addr1Balance = await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address);
expect(addr1Balance).to.equal(ethers.parseEther("100"));
const addr2Balance = await myToken.balanceOf(addr2.address);
expect(addr2Balance).to.equal(ethers.parseEther("50"));
});
});
describe("Allowances", function () {
it("Should approve tokens for delegated transfer", async function () {
await myToken.approve(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
const allowance = await myToken.allowance(owner.address, addr1.address);
expect(allowance).to.equal(ethers.parseEther("100"));
});
it("Should transfer tokens using transferFrom", async function () {
// Approve addr1 to spend 100 tokens
await myToken.approve(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
// addr1 transfers tokens from owner to addr2
await myToken.connect(addr1).transferFrom(
owner.address,
addr2.address,
ethers.parseEther("50")
);
// Check balances
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr2.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("50")
);
// Check remaining allowance
expect(await myToken.allowance(owner.address, addr1.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("50")
);
});
it("Should fail transferFrom without approval", async function () {
await expect(
myToken.connect(addr1).transferFrom(
owner.address,
addr2.address,
ethers.parseEther("50")
)
).to.be.revertedWithCustomError(myToken, "ERC20InsufficientAllowance");
});
});
describe("Minting", function () {
it("Should allow owner to mint tokens", async function () {
const initialSupply = await myToken.totalSupply();
await myToken.mint(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"));
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("1000")
);
expect(await myToken.totalSupply()).to.equal(
initialSupply + ethers.parseEther("1000")
);
});
it("Should prevent non-owner from minting", async function () {
await expect(
myToken.connect(addr1).mint(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"))
).to.be.revertedWithCustomError(myToken, "OwnableUnauthorizedAccount");
});
it("Should not exceed max supply", async function () {
const maxSupply = await myToken.MAX_SUPPLY();
const currentSupply = await myToken.totalSupply();
const remaining = maxSupply - currentSupply;
// Try to mint more than remaining supply
await expect(
myToken.mint(addr1.address, remaining + ethers.parseEther("1"))
).to.be.revertedWith("Exceeds max supply");
});
});
describe("Burning", function () {
it("Should allow token holders to burn their tokens", async function () {
// Transfer tokens to addr1
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"));
const initialSupply = await myToken.totalSupply();
const initialBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address);
// Burn 500 tokens
await myToken.connect(addr1).burn(ethers.parseEther("500"));
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address)).to.equal(
initialBalance - ethers.parseEther("500")
);
expect(await myToken.totalSupply()).to.equal(
initialSupply - ethers.parseEther("500")
);
});
});
describe("Pausable", function () {
it("Should pause and unpause transfers", async function () {
await myToken.pause();
await expect(
myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"))
).to.be.revertedWithCustomError(myToken, "EnforcedPause");
await myToken.unpause();
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("100")
);
});
});
describe("Blacklist", function () {
it("Should prevent blacklisted addresses from transferring", async function () {
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"));
await myToken.blacklist(addr1.address);
await expect(
myToken.connect(addr1).transfer(addr2.address, ethers.parseEther("100"))
).to.be.revertedWith("Sender is blacklisted");
});
it("Should allow whitelisting previously blacklisted addresses", async function () {
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"));
await myToken.blacklist(addr1.address);
await myToken.whitelist(addr1.address);
await myToken.connect(addr1).transfer(addr2.address, ethers.parseEther("100"));
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr2.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("100")
);
});
});
describe("Transfer Fees", function () {
it("Should deduct transfer fee when set", async function () {
// Set 1% fee
await myToken.setTransferFee(100); // 100 basis points = 1%
const initialOwnerBalance = await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address);
await myToken.transfer(addr1.address, ethers.parseEther("1000"));
// addr1 should receive 990 tokens (1% fee = 10 tokens)
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(addr1.address)).to.equal(
ethers.parseEther("990")
);
// Fee recipient (owner) should receive the fee
expect(await myToken.balanceOf(owner.address)).to.equal(
initialOwnerBalance - ethers.parseEther("1000") + ethers.parseEther("10")
);
});
});
});
Running Tests
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Run all tests
npx hardhat test
# Run specific test file
npx hardhat test test/MyToken.test.js
# Run with gas reporting
REPORT_GAS=true npx hardhat test
# Run with coverage
npx hardhat coverage
Deployment
Hardhat Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// hardhat.config.js
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("dotenv").config();
module.exports = {
solidity: {
version: "0.8.20",
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200
}
}
},
networks: {
hardhat: {
chainId: 31337
},
sepolia: {
url: process.env.SEPOLIA_RPC_URL,
accounts: [process.env.PRIVATE_KEY],
chainId: 11155111
},
mainnet: {
url: process.env.MAINNET_RPC_URL,
accounts: [process.env.PRIVATE_KEY],
chainId: 1
}
},
etherscan: {
apiKey: process.env.ETHERSCAN_API_KEY
}
};
Environment Variables
1
2
3
4
5
# .env
SEPOLIA_RPC_URL=https://eth-sepolia.g.alchemy.com/v2/YOUR_API_KEY
MAINNET_RPC_URL=https://eth-mainnet.g.alchemy.com/v2/YOUR_API_KEY
PRIVATE_KEY=your_private_key_here
ETHERSCAN_API_KEY=your_etherscan_api_key
Deployment Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
// scripts/deploy.js
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
console.log("Deploying MyToken...");
// Get the deployer account
const [deployer] = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
console.log("Deploying with account:", deployer.address);
// Check balance
const balance = await hre.ethers.provider.getBalance(deployer.address);
console.log("Account balance:", hre.ethers.formatEther(balance), "ETH");
// Deploy the contract
const MyToken = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("MyToken");
const myToken = await MyToken.deploy(deployer.address);
await myToken.waitForDeployment();
const address = await myToken.getAddress();
console.log("MyToken deployed to:", address);
// Wait for block confirmations
console.log("Waiting for block confirmations...");
await myToken.deploymentTransaction().wait(5);
// Verify contract on Etherscan
console.log("Verifying contract on Etherscan...");
try {
await hre.run("verify:verify", {
address: address,
constructorArguments: [deployer.address],
});
console.log("Contract verified successfully");
} catch (error) {
console.log("Verification error:", error.message);
}
// Log initial state
console.log("\nToken Details:");
console.log("Name:", await myToken.name());
console.log("Symbol:", await myToken.symbol());
console.log("Decimals:", await myToken.decimals());
console.log("Total Supply:", hre.ethers.formatEther(await myToken.totalSupply()));
console.log("Owner Balance:", hre.ethers.formatEther(await myToken.balanceOf(deployer.address)));
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Deploy Commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Deploy to local network
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network hardhat
# Deploy to Sepolia testnet
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network sepolia
# Deploy to mainnet (be careful!)
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network mainnet
# Verify contract manually
npx hardhat verify --network sepolia CONTRACT_ADDRESS "CONSTRUCTOR_ARGS"
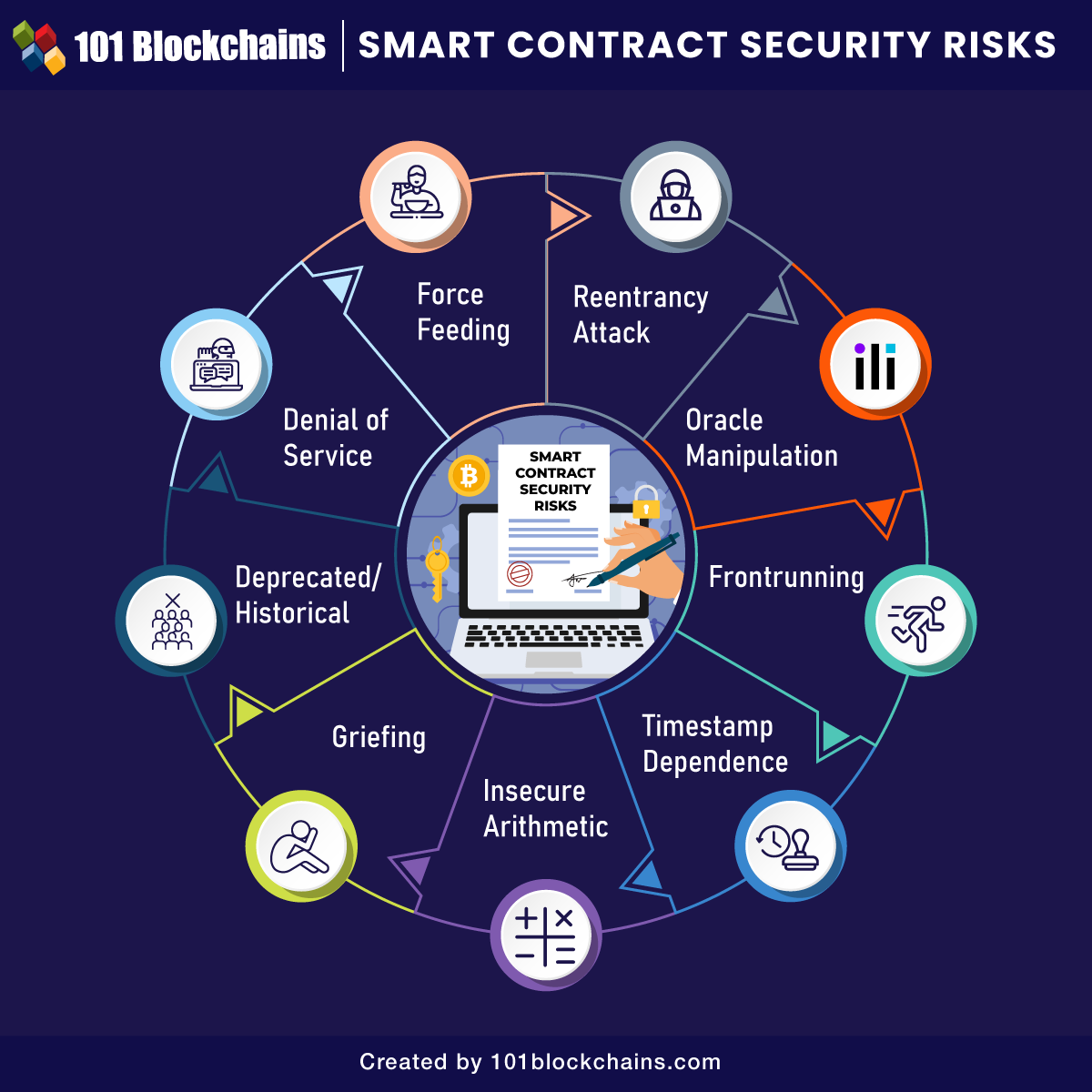
Security Considerations
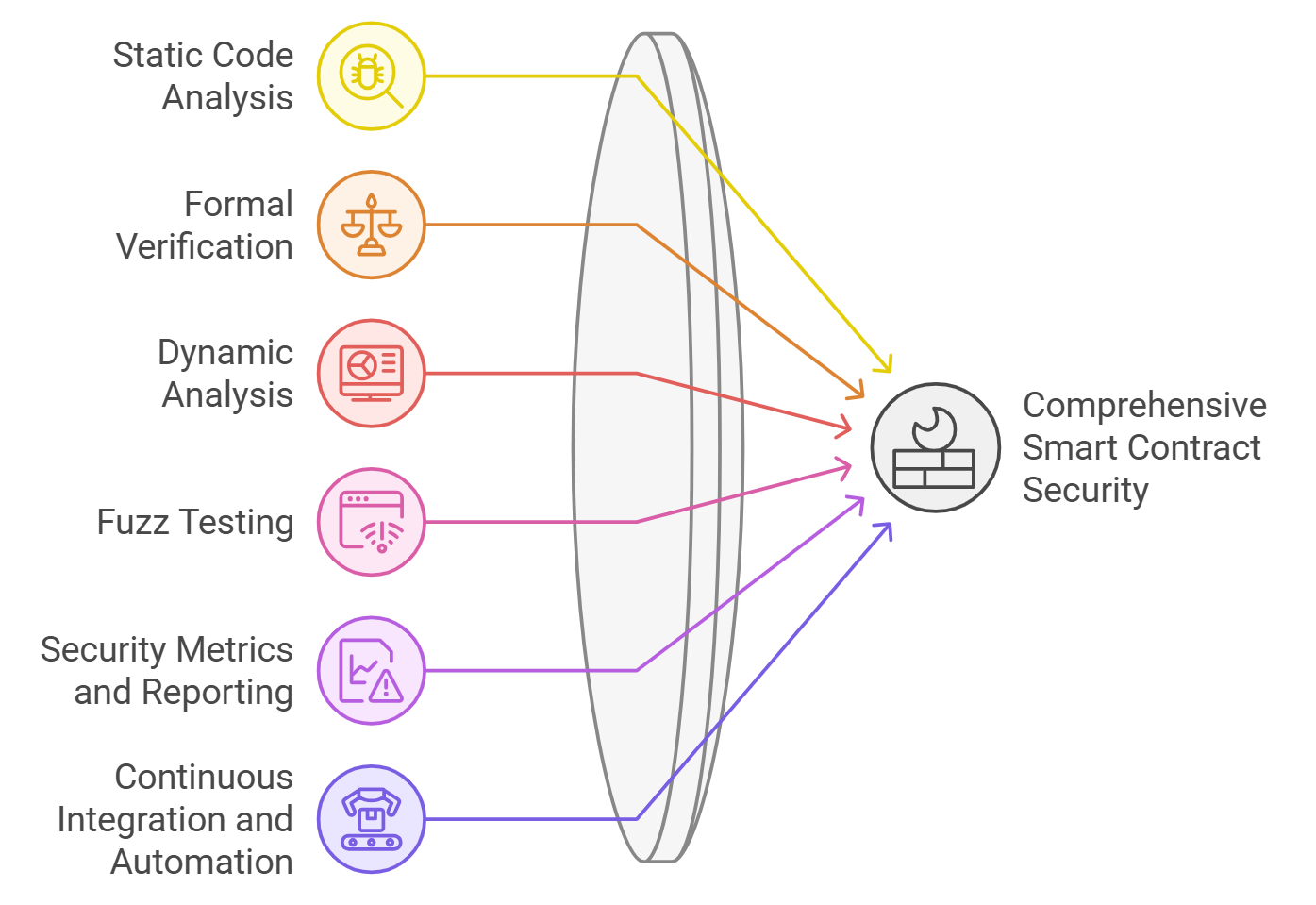 Figure 3: Smart contract security testing workflow
Figure 3: Smart contract security testing workflow
Common Vulnerabilities
1. Reentrancy Attacks
While ERC-20 tokens are less susceptible to reentrancy than contracts handling ETH, it’s still important to follow checks-effects-interactions pattern:
// Vulnerable code
function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) public {
balanceOf[to] += amount; // State change after external call risk
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= amount;
// If 'to' is a contract, it could reenter
}
// Safe code
function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) public {
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= amount, "Insufficient balance");
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= amount; // State changes first
balanceOf[to] += amount;
emit Transfer(msg.sender, to, amount);
}
2. Integer Overflow/Underflow
Solidity 0.8.0+ includes automatic overflow checks, but be aware when using unchecked blocks:
// Safe in Solidity 0.8.0+
function safeAdd(uint256 a, uint256 b) public pure returns (uint256) {
return a + b; // Will revert on overflow
}
// Unsafe if you disable checks
function unsafeAdd(uint256 a, uint256 b) public pure returns (uint256) {
unchecked {
return a + b; // Could overflow silently
}
}
3. Approval Race Condition
The ERC-20 approve function has a known race condition:
// Problem: If you want to change approval from 100 to 50,
// the spender could spend 100 before your transaction confirms,
// then spend another 50 after
// Solution: Use increaseAllowance and decreaseAllowance
function increaseAllowance(address spender, uint256 addedValue) public returns (bool) {
_approve(msg.sender, spender, allowance[msg.sender][spender] + addedValue);
return true;
}
function decreaseAllowance(address spender, uint256 subtractedValue) public returns (bool) {
uint256 currentAllowance = allowance[msg.sender][spender];
require(currentAllowance >= subtractedValue, "Decreased allowance below zero");
_approve(msg.sender, spender, currentAllowance - subtractedValue);
return true;
}
Security Best Practices
1. Use OpenZeppelin Contracts
// Always use audited, battle-tested implementations
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
2. Implement Access Control
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/AccessControl.sol";
contract SecureToken is ERC20, AccessControl {
bytes32 public constant MINTER_ROLE = keccak256("MINTER_ROLE");
bytes32 public constant BURNER_ROLE = keccak256("BURNER_ROLE");
constructor() ERC20("Secure Token", "SEC") {
_grantRole(DEFAULT_ADMIN_ROLE, msg.sender);
_grantRole(MINTER_ROLE, msg.sender);
}
function mint(address to, uint256 amount) public onlyRole(MINTER_ROLE) {
_mint(to, amount);
}
}
3. Add Circuit Breakers
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/security/Pausable.sol";
contract PausableToken is ERC20, Pausable, Ownable {
function pause() public onlyOwner {
_pause();
}
function unpause() public onlyOwner {
_unpause();
}
function _beforeTokenTransfer(
address from,
address to,
uint256 amount
) internal override whenNotPaused {
super._beforeTokenTransfer(from, to, amount);
}
}
4. Implement Rate Limiting
contract RateLimitedToken is ERC20 {
mapping(address => uint256) public lastTransferTime;
uint256 public constant TRANSFER_COOLDOWN = 1 minutes;
function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) public override returns (bool) {
require(
block.timestamp >= lastTransferTime[msg.sender] + TRANSFER_COOLDOWN,
"Transfer cooldown active"
);
lastTransferTime[msg.sender] = block.timestamp;
return super.transfer(to, amount);
}
}
Advanced Features
Snapshot Functionality
Track token balances at specific blocks for governance:
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Snapshot.sol";
contract SnapshotToken is ERC20, ERC20Snapshot, Ownable {
constructor() ERC20("Snapshot Token", "SNAP") {
_mint(msg.sender, 1000000 * 10**decimals());
}
function snapshot() public onlyOwner returns (uint256) {
return _snapshot();
}
function _beforeTokenTransfer(
address from,
address to,
uint256 amount
) internal override(ERC20, ERC20Snapshot) {
super._beforeTokenTransfer(from, to, amount);
}
}
Capped Supply
Prevent unlimited inflation:
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Capped.sol";
contract CappedToken is ERC20, ERC20Capped, Ownable {
constructor()
ERC20("Capped Token", "CAP")
ERC20Capped(1000000 * 10**decimals()) // 1M cap
{
_mint(msg.sender, 500000 * 10**decimals()); // 500K initial
}
function mint(address to, uint256 amount) public onlyOwner {
_mint(to, amount);
}
function _mint(address account, uint256 amount)
internal
override(ERC20, ERC20Capped)
{
super._mint(account, amount);
}
}
Voting and Governance
Enable on-chain governance:
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Votes.sol";
contract GovernanceToken is ERC20, ERC20Votes, Ownable {
constructor()
ERC20("Governance Token", "GOV")
ERC20Permit("Governance Token")
{
_mint(msg.sender, 10000000 * 10**decimals());
}
// Required overrides
function _afterTokenTransfer(
address from,
address to,
uint256 amount
) internal override(ERC20, ERC20Votes) {
super._afterTokenTransfer(from, to, amount);
}
function _mint(address to, uint256 amount)
internal
override(ERC20, ERC20Votes)
{
super._mint(to, amount);
}
function _burn(address account, uint256 amount)
internal
override(ERC20, ERC20Votes)
{
super._burn(account, amount);
}
}
Frontend Integration
Web3.js Integration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
// frontend/src/token.js
const Web3 = require('web3');
const tokenABI = require('./MyToken.json').abi;
class TokenInterface {
constructor(contractAddress, providerURL) {
this.web3 = new Web3(providerURL);
this.contract = new this.web3.eth.Contract(tokenABI, contractAddress);
}
// Get token balance
async getBalance(address) {
const balance = await this.contract.methods.balanceOf(address).call();
return this.web3.utils.fromWei(balance, 'ether');
}
// Transfer tokens
async transfer(from, to, amount, privateKey) {
const amountWei = this.web3.utils.toWei(amount.toString(), 'ether');
const tx = {
from: from,
to: this.contract.options.address,
data: this.contract.methods.transfer(to, amountWei).encodeABI(),
gas: 100000
};
const signedTx = await this.web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(tx, privateKey);
const receipt = await this.web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(signedTx.rawTransaction);
return receipt;
}
// Approve spender
async approve(owner, spender, amount, privateKey) {
const amountWei = this.web3.utils.toWei(amount.toString(), 'ether');
const tx = {
from: owner,
to: this.contract.options.address,
data: this.contract.methods.approve(spender, amountWei).encodeABI(),
gas: 100000
};
const signedTx = await this.web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(tx, privateKey);
const receipt = await this.web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(signedTx.rawTransaction);
return receipt;
}
// Get allowance
async getAllowance(owner, spender) {
const allowance = await this.contract.methods.allowance(owner, spender).call();
return this.web3.utils.fromWei(allowance, 'ether');
}
// Listen to Transfer events
watchTransfers(callback) {
this.contract.events.Transfer({
fromBlock: 'latest'
})
.on('data', (event) => {
callback({
from: event.returnValues.from,
to: event.returnValues.to,
value: this.web3.utils.fromWei(event.returnValues.value, 'ether'),
transactionHash: event.transactionHash
});
})
.on('error', console.error);
}
}
// Usage example
const token = new TokenInterface(
'0xYourTokenAddress',
'https://eth-mainnet.g.alchemy.com/v2/YOUR_API_KEY'
);
// Get balance
token.getBalance('0xUserAddress').then(balance => {
console.log('Balance:', balance);
});
React Integration with ethers.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
// frontend/src/components/TokenDashboard.jsx
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import MyTokenABI from '../contracts/MyToken.json';
function TokenDashboard() {
const [balance, setBalance] = useState('0');
const [totalSupply, setTotalSupply] = useState('0');
const [account, setAccount] = useState('');
const [contract, setContract] = useState(null);
const contractAddress = '0xYourTokenAddress';
useEffect(() => {
initializeContract();
}, []);
async function initializeContract() {
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
try {
// Request account access
await window.ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_requestAccounts' });
// Create provider and signer
const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
const signer = await provider.getSigner();
const userAddress = await signer.getAddress();
// Create contract instance
const tokenContract = new ethers.Contract(
contractAddress,
MyTokenABI.abi,
signer
);
setAccount(userAddress);
setContract(tokenContract);
// Load initial data
await loadTokenData(tokenContract, userAddress);
// Listen for account changes
window.ethereum.on('accountsChanged', handleAccountChange);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error initializing contract:', error);
}
} else {
alert('Please install MetaMask!');
}
}
async function loadTokenData(tokenContract, userAddress) {
try {
const userBalance = await tokenContract.balanceOf(userAddress);
const supply = await tokenContract.totalSupply();
setBalance(ethers.formatEther(userBalance));
setTotalSupply(ethers.formatEther(supply));
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error loading token data:', error);
}
}
async function handleTransfer(to, amount) {
if (!contract) return;
try {
const amountWei = ethers.parseEther(amount);
const tx = await contract.transfer(to, amountWei);
console.log('Transaction sent:', tx.hash);
await tx.wait();
console.log('Transaction confirmed!');
// Reload balance
await loadTokenData(contract, account);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Transfer error:', error);
alert('Transfer failed: ' + error.message);
}
}
function handleAccountChange(accounts) {
if (accounts.length === 0) {
console.log('Please connect to MetaMask');
} else {
setAccount(accounts[0]);
if (contract) {
loadTokenData(contract, accounts[0]);
}
}
}
return (
<div className="token-dashboard">
<h2>My Token Dashboard</h2>
<div className="account-info">
<p><strong>Connected Account:</strong> {account}</p>
<p><strong>Your Balance:</strong> {balance} MTK</p>
<p><strong>Total Supply:</strong> {totalSupply} MTK</p>
</div>
<div className="transfer-form">
<h3>Transfer Tokens</h3>
<form onSubmit={(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const to = e.target.recipient.value;
const amount = e.target.amount.value;
handleTransfer(to, amount);
}}>
<input
type="text"
name="recipient"
placeholder="Recipient Address"
required
/>
<input
type="number"
name="amount"
placeholder="Amount"
step="0.01"
required
/>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default TokenDashboard;
Gas Optimization
Optimization Techniques
1. Use Efficient Data Types
// Less efficient
uint256 public value1;
uint256 public value2;
uint256 public value3;
// More efficient (packed into single storage slot)
uint128 public value1;
uint64 public value2;
uint64 public value3;
2. Batch Operations
// Inefficient: Multiple transactions
function transferMultiple(address[] memory recipients, uint256[] memory amounts) public {
for (uint i = 0; i < recipients.length; i++) {
transfer(recipients[i], amounts[i]);
}
}
// Efficient: Single transaction with batch transfer
function batchTransfer(address[] calldata recipients, uint256[] calldata amounts)
external
returns (bool)
{
require(recipients.length == amounts.length, "Arrays length mismatch");
require(recipients.length <= 200, "Too many recipients");
uint256 totalAmount = 0;
for (uint i = 0; i < amounts.length; i++) {
totalAmount += amounts[i];
}
require(balanceOf(msg.sender) >= totalAmount, "Insufficient balance");
for (uint i = 0; i < recipients.length; i++) {
_transfer(msg.sender, recipients[i], amounts[i]);
}
return true;
}
3. Use Calldata Instead of Memory
// More expensive
function processData(uint256[] memory data) public {
// process data
}
// Cheaper
function processData(uint256[] calldata data) external {
// process data
}
Conclusion
Implementing an ERC-20 token is a fundamental skill for blockchain developers. Throughout this guide, we’ve covered:
- Standard Compliance: Understanding the ERC-20 specification and its required functions
- Basic Implementation: Building a simple token from scratch
- Advanced Features: Adding minting, burning, pausing, and governance capabilities
- Security: Implementing best practices and avoiding common vulnerabilities
- Testing: Comprehensive test suites to ensure contract reliability
- Deployment: Deploying to testnets and mainnet with verification
- Integration: Connecting tokens to frontend applications
- Optimization: Gas-efficient patterns and techniques
Key Takeaways:
- Always use audited libraries like OpenZeppelin
- Test extensively before mainnet deployment
- Implement proper access control and security features
- Consider gas optimization from the start
- Plan tokenomics carefully (supply caps, inflation, etc.)
- Document your contract thoroughly
- Get professional audits for production tokens
ERC-20 tokens power much of the DeFi ecosystem, from stablecoins to governance tokens. By mastering this standard, you’re equipped to build the next generation of blockchain applications.
Resources
Official Documentation
- EIP-20: Token Standard
- OpenZeppelin ERC20 Documentation
- Ethereum Development Documentation
- Solidity Documentation
Development Tools
- Hardhat - Ethereum development environment
- Remix IDE - Browser-based Solidity IDE
- Etherscan - Blockchain explorer and verification
- Tenderly - Smart contract monitoring
Security Resources
- OpenZeppelin Security
- Smart Contract Weakness Classification
- Consensys Smart Contract Best Practices
- Slither - Static analysis tool
Learning Platforms
- CryptoZombies - Learn Solidity by building games
- Ethernaut - Security-focused challenges
- Solidity by Example
- Alchemy University
Community
- Ethereum Stack Exchange
- OpenZeppelin Forum
- r/ethdev - Ethereum development subreddit
Build responsibly, test thoroughly, and welcome to the world of token development! 🚀