FastAPI ile Asenkron Web Servisleri Geliştirme
FastAPI ile yüksek performanslı asenkron web servisleri. Async/await, WebSocket, dependency injection, authentication ve production deployment.
Modern web uygulamaları için yüksek performans ve ölçeklenebilirlik kritik önem taşır. FastAPI, Python ekosisteminde asenkron programlama yetenekleriyle öne çıkan ve hem geliştirici deneyimini hem de uygulama performansını optimize eden bir web framework’üdür. Bu yazıda FastAPI ile asenkron web servisleri geliştirmeyi, async/await desenlerini ve production-ready uygulamalar için best practice’leri detaylıca inceleyeceğiz.
FastAPI Nedir ve Neden Tercih Edilmeli?
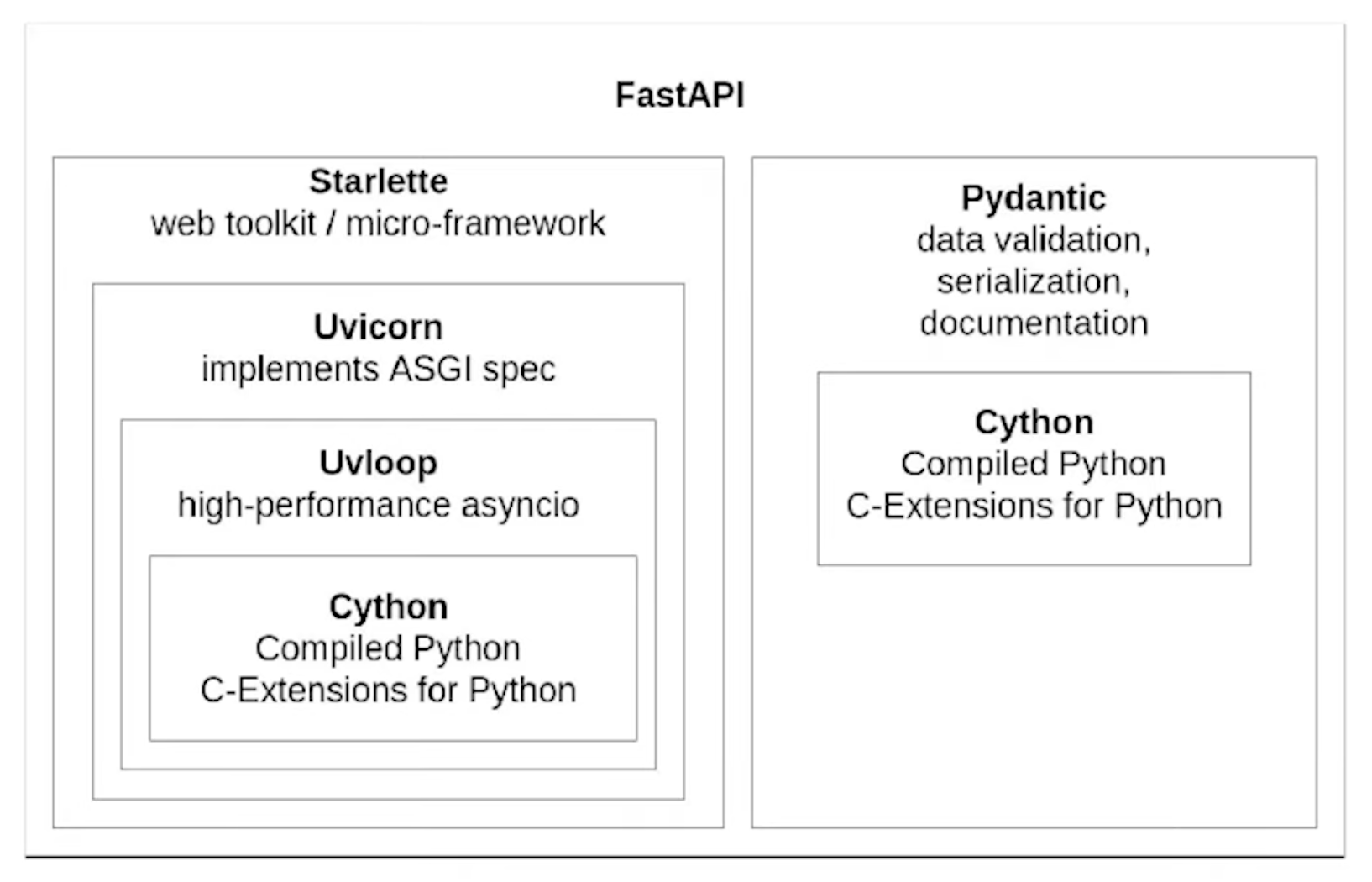
FastAPI, Python’ın type hint sistemini kullanan, otomatik API dokümantasyonu üreten ve asenkron işlemleri destekleyen modern bir web framework’üdür. Starlette ve Pydantic kütüphanelerinin gücünü bir araya getirerek geliştiricilere hem hızlı hem de güvenilir API’ler oluşturma imkanı sunar.
FastAPI’nin Temel Özellikleri
- Yüksek Performans: Node.js ve Go ile yarışacak seviyede hız
- Otomatik Dokümantasyon: Swagger UI ve ReDoc entegrasyonu
- Type Safety: Python type hints ile compile-time hata yakalama
- Asenkron Destek: Async/await ile non-blocking I/O işlemleri
- Kolay Validasyon: Pydantic modelleri ile otomatik veri doğrulama
Kurulum ve İlk Adımlar
FastAPI ile çalışmaya başlamak için gerekli paketleri kuralım:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# FastAPI ve ASGI sunucusu kurulumu
pip install fastapi uvicorn[standard]
# Asenkron HTTP istekleri için
pip install httpx aiofiles
# Veritabanı işlemleri için (opsiyonel)
pip install sqlalchemy databases asyncpg
Basit Bir FastAPI Uygulaması
İlk FastAPI uygulamamızı oluşturalım:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
# FastAPI uygulaması oluşturma
app = FastAPI(
title="Asenkron API",
description="FastAPI ile asenkron web servisleri",
version="1.0.0"
)
# Pydantic model ile request body validasyonu
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
# Basit GET endpoint
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "FastAPI Asenkron API"}
# POST endpoint ile veri işleme
@app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item):
# Otomatik validasyon ve serializasyon
item_dict = item.dict()
if item.tax:
price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax
item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})
return item_dict
# Path parametresi ve query parametresi
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str | None = None):
result = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
result.update({"q": q})
return result
Uygulamayı çalıştırmak için:
1
2
3
4
5
# Development modunda çalıştırma (auto-reload aktif)
uvicorn main:app --reload --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# Production modunda çalıştırma
uvicorn main:app --workers 4 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
Tarayıcınızda http://localhost:8000/docs adresini ziyaret ederek otomatik oluşturulan Swagger UI dokümantasyonunu görebilirsiniz.
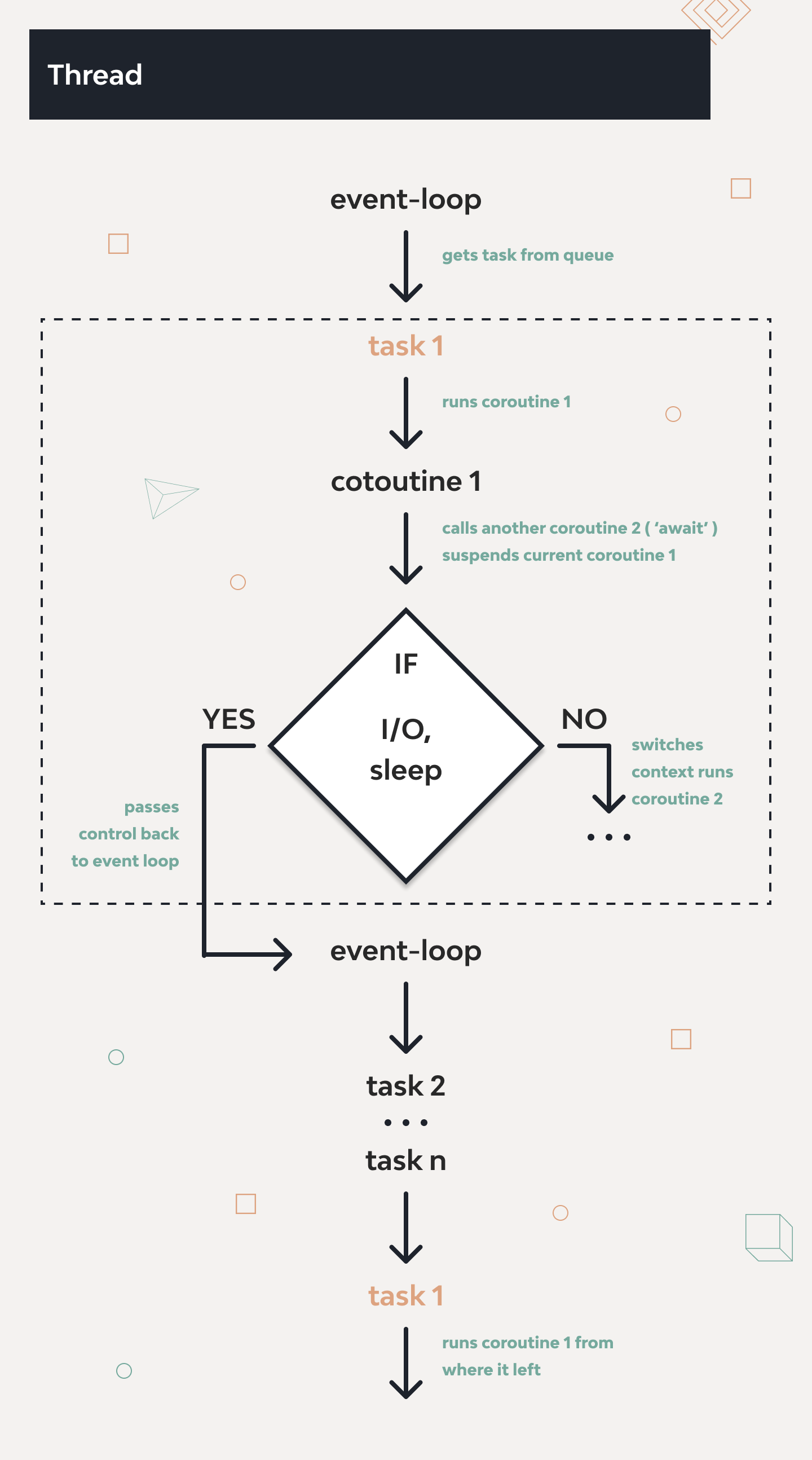 AsyncIO Event Loop ve Asenkron İşlem Akışı
AsyncIO Event Loop ve Asenkron İşlem Akışı
Asenkron Programlama Temelleri
FastAPI’nin gücü, Python’ın asyncio kütüphanesinden gelir. Asenkron programlama, I/O işlemlerinin tamamlanmasını beklerken diğer görevlerin yürütülmesine izin verir.
Sync vs Async Karşılaştırması
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
import time
import asyncio
import httpx
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
# Senkron (Blocking) endpoint
@app.get("/sync")
def sync_endpoint():
# 3 farklı API'ye sırayla istek atıyoruz
total_time = 0
results = []
for i in range(3):
start = time.time()
# Bloklanma: Bu istek bitene kadar bekle
response = httpx.get(f"https://api.example.com/data/{i}")
elapsed = time.time() - start
total_time += elapsed
results.append(response.json())
return {
"results": results,
"total_time": f"{total_time:.2f}s",
"type": "synchronous"
}
# Asenkron (Non-blocking) endpoint
@app.get("/async")
async def async_endpoint():
start_time = time.time()
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
# Tüm istekleri eşzamanlı olarak başlat
tasks = [
client.get(f"https://api.example.com/data/{i}")
for i in range(3)
]
# Tüm isteklerin tamamlanmasını bekle
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
results = [r.json() for r in responses]
total_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
"results": results,
"total_time": f"{total_time:.2f}s",
"type": "asynchronous"
}
Bu örnekte, sync endpoint her istek için yaklaşık 1 saniye beklerse toplamda 3 saniye sürerken, async endpoint tüm istekleri paralel başlattığı için sadece 1 saniye sürer.
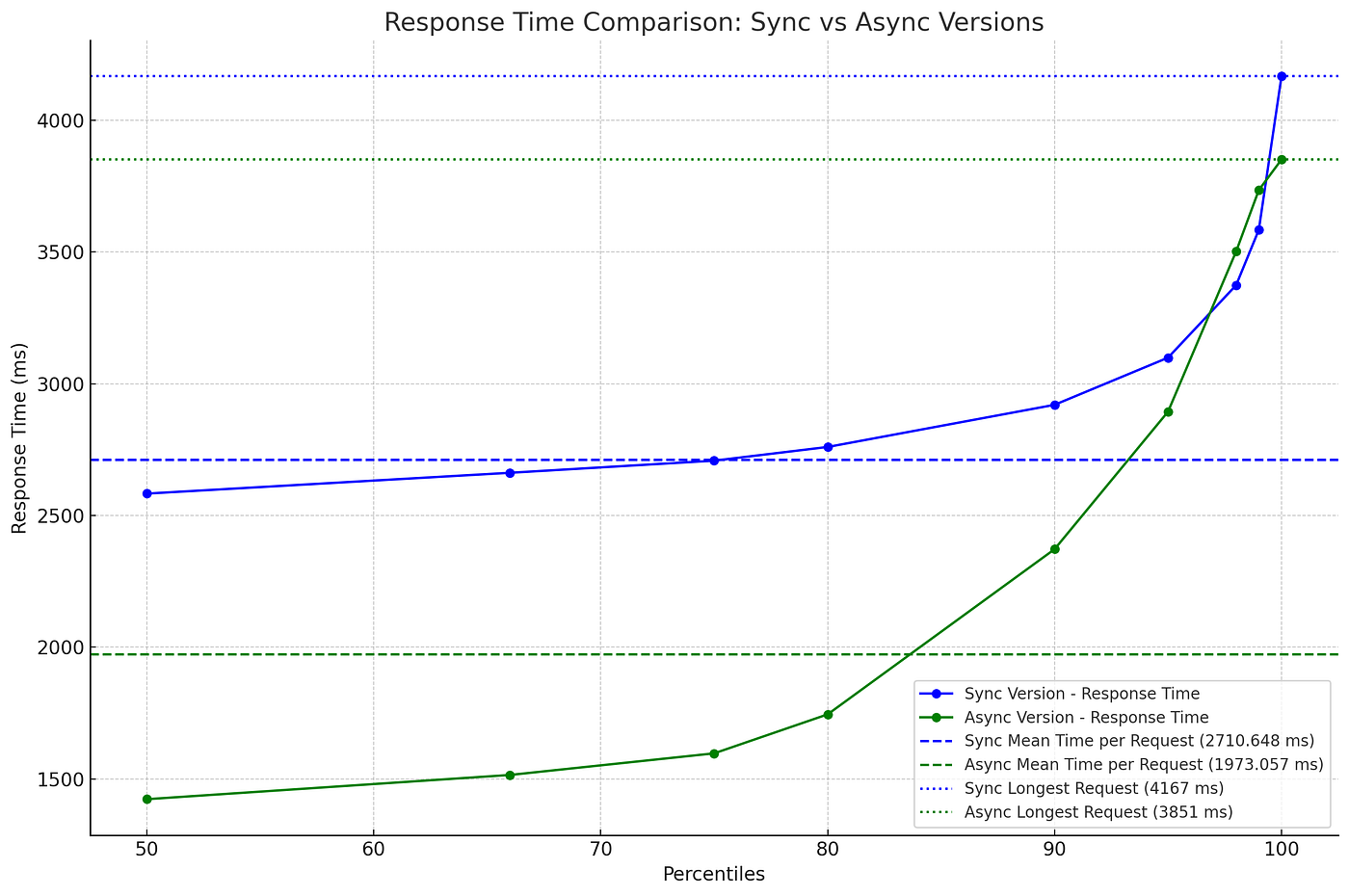 Senkron ve Asenkron API Performans Karşılaştırması
Senkron ve Asenkron API Performans Karşılaştırması
Asenkron Veritabanı İşlemleri
Veritabanı işlemleri genellikle uygulamanın en yavaş kısmıdır. Asenkron veritabanı bağlantıları kullanarak performansı önemli ölçüde artırabiliriz.
SQLAlchemy ile Async Database
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import create_async_engine, AsyncSession
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import async_sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.orm import DeclarativeBase, Mapped, mapped_column
from sqlalchemy import select
from typing import AsyncGenerator
from fastapi import Depends
# Database URL (PostgreSQL için asyncpg driver)
DATABASE_URL = "postgresql+asyncpg://user:password@localhost/dbname"
# Async engine oluşturma
engine = create_async_engine(
DATABASE_URL,
echo=True, # SQL sorgularını logla
pool_size=5, # Connection pool boyutu
max_overflow=10 # Pool doluysa ekstra bağlantı sayısı
)
# Session factory
async_session_maker = async_sessionmaker(
engine,
class_=AsyncSession,
expire_on_commit=False
)
# Base model
class Base(DeclarativeBase):
pass
# User model örneği
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = "users"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
username: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(unique=True, index=True)
email: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(unique=True)
full_name: Mapped[str | None]
is_active: Mapped[bool] = mapped_column(default=True)
# Database session dependency
async def get_db() -> AsyncGenerator[AsyncSession, None]:
async with async_session_maker() as session:
try:
yield session
await session.commit()
except Exception:
await session.rollback()
raise
finally:
await session.close()
# FastAPI endpoints
from pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStr
class UserCreate(BaseModel):
username: str
email: EmailStr
full_name: str | None = None
class UserResponse(BaseModel):
id: int
username: str
email: str
full_name: str | None
is_active: bool
class Config:
from_attributes = True
@app.post("/users/", response_model=UserResponse)
async def create_user(
user_data: UserCreate,
db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)
):
# Yeni kullanıcı oluştur
new_user = User(
username=user_data.username,
email=user_data.email,
full_name=user_data.full_name
)
db.add(new_user)
await db.flush() # ID'yi almak için flush
await db.refresh(new_user) # Objeyi yenile
return new_user
@app.get("/users/{user_id}", response_model=UserResponse)
async def get_user(
user_id: int,
db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)
):
# Async query execution
result = await db.execute(
select(User).where(User.id == user_id)
)
user = result.scalar_one_or_none()
if not user:
from fastapi import HTTPException
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="User not found")
return user
@app.get("/users/", response_model=list[UserResponse])
async def list_users(
skip: int = 0,
limit: int = 100,
db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)
):
# Pagination ile kullanıcı listesi
result = await db.execute(
select(User)
.offset(skip)
.limit(limit)
.order_by(User.id)
)
users = result.scalars().all()
return users
Database Connection Pooling
Connection pool ayarları performans için kritiktir:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
from sqlalchemy.pool import NullPool, QueuePool
# Production için önerilen ayarlar
engine = create_async_engine(
DATABASE_URL,
echo=False, # Production'da False olmalı
pool_size=20, # Maksimum pool boyutu
max_overflow=10, # Pool doluysa ekstra bağlantı
pool_timeout=30, # Bağlantı bekleme süresi (saniye)
pool_recycle=3600, # Bağlantıları yeniden kullanım süresi
pool_pre_ping=True, # Bağlantı sağlığını kontrol et
poolclass=QueuePool # Default pool class
)
WebSocket ile Gerçek Zamanlı İletişim
FastAPI, WebSocket protokolünü native olarak destekler ve gerçek zamanlı uygulamalar için ideal bir çözümdür.
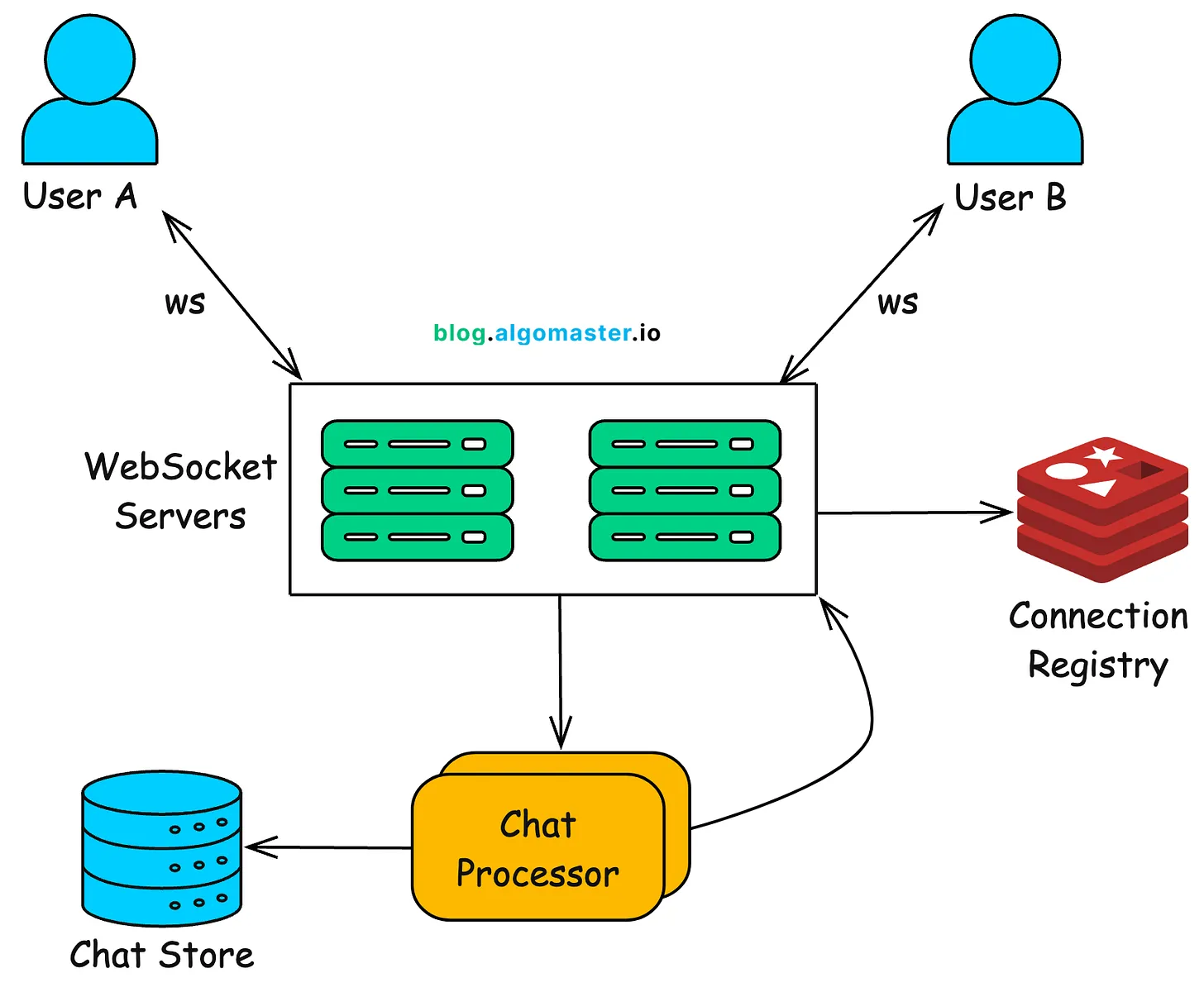 WebSocket Bağlantısı ve Gerçek Zamanlı İletişim Mimarisi
WebSocket Bağlantısı ve Gerçek Zamanlı İletişim Mimarisi
Basit WebSocket Sunucusu
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
from fastapi import WebSocket, WebSocketDisconnect
from typing import List
import json
import asyncio
class ConnectionManager:
def __init__(self):
# Aktif bağlantıları sakla
self.active_connections: List[WebSocket] = []
async def connect(self, websocket: WebSocket):
# Yeni bağlantıyı kabul et
await websocket.accept()
self.active_connections.append(websocket)
print(f"Client connected. Total: {len(self.active_connections)}")
def disconnect(self, websocket: WebSocket):
# Bağlantıyı kaldır
self.active_connections.remove(websocket)
print(f"Client disconnected. Total: {len(self.active_connections)}")
async def send_personal_message(self, message: str, websocket: WebSocket):
# Tek bir client'a mesaj gönder
await websocket.send_text(message)
async def broadcast(self, message: str):
# Tüm bağlı client'lara mesaj gönder
for connection in self.active_connections:
try:
await connection.send_text(message)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error broadcasting to client: {e}")
manager = ConnectionManager()
@app.websocket("/ws/{client_id}")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket, client_id: int):
await manager.connect(websocket)
try:
# Hoş geldin mesajı gönder
await manager.send_personal_message(
json.dumps({
"type": "connection",
"message": f"Welcome! Your ID: {client_id}"
}),
websocket
)
# Diğer client'lara bildir
await manager.broadcast(
json.dumps({
"type": "user_joined",
"client_id": client_id
})
)
# Mesajları sürekli dinle
while True:
# Client'tan mesaj al
data = await websocket.receive_text()
# Mesajı işle
message_data = json.loads(data)
# Tüm client'lara yayınla
await manager.broadcast(
json.dumps({
"type": "message",
"client_id": client_id,
"message": message_data.get("message", "")
})
)
except WebSocketDisconnect:
manager.disconnect(websocket)
# Diğer client'lara bildir
await manager.broadcast(
json.dumps({
"type": "user_left",
"client_id": client_id
})
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"WebSocket error: {e}")
manager.disconnect(websocket)
WebSocket Client Örneği
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
async def websocket_client():
uri = "ws://localhost:8000/ws/123"
async with websockets.connect(uri) as websocket:
# Mesaj gönder
await websocket.send(json.dumps({
"message": "Hello from client!"
}))
# Mesajları dinle
async for message in websocket:
data = json.loads(message)
print(f"Received: {data}")
# Client'ı çalıştır
asyncio.run(websocket_client())
Middleware ve Request/Response İşleme
FastAPI’de middleware’ler, her request ve response üzerinde işlem yapmanıza olanak tanır.
Custom Middleware Oluşturma
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
from fastapi import Request
from starlette.middleware.base import BaseHTTPMiddleware
import time
import logging
# Logger ayarla
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class TimingMiddleware(BaseHTTPMiddleware):
async def dispatch(self, request: Request, call_next):
# Request başlangıç zamanı
start_time = time.time()
# Request bilgilerini logla
logger.info(f"Request: {request.method} {request.url.path}")
# Response'u al
response = await call_next(request)
# İşlem süresini hesapla
process_time = time.time() - start_time
# Response header'ına ekle
response.headers["X-Process-Time"] = str(process_time)
# Loglama
logger.info(
f"Response: {response.status_code} | "
f"Time: {process_time:.3f}s"
)
return response
class RateLimitMiddleware(BaseHTTPMiddleware):
def __init__(self, app, max_requests: int = 100, window: int = 60):
super().__init__(app)
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.window = window
self.requests = {} # {ip: [(timestamp, count)]}
async def dispatch(self, request: Request, call_next):
# Client IP adresini al
client_ip = request.client.host
current_time = time.time()
# Eski kayıtları temizle
if client_ip in self.requests:
self.requests[client_ip] = [
(ts, count) for ts, count in self.requests[client_ip]
if current_time - ts < self.window
]
# Request sayısını kontrol et
request_count = sum(
count for _, count in self.requests.get(client_ip, [])
)
if request_count >= self.max_requests:
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
return JSONResponse(
status_code=429,
content={
"error": "Too many requests",
"retry_after": self.window
}
)
# Yeni request'i kaydet
if client_ip not in self.requests:
self.requests[client_ip] = []
self.requests[client_ip].append((current_time, 1))
# Response'u döndür
response = await call_next(request)
return response
# Middleware'leri ekle
app.add_middleware(TimingMiddleware)
app.add_middleware(RateLimitMiddleware, max_requests=100, window=60)
CORS Ayarları
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
# CORS middleware ekle
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["https://example.com", "https://app.example.com"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"], # Tüm HTTP metodlarına izin ver
allow_headers=["*"], # Tüm header'lara izin ver
expose_headers=["X-Process-Time"] # Client'a expose edilecek header'lar
)
Background Tasks ve Asenkron Görevler
Bazı işlemler response döndürüldükten sonra arka planda yapılabilir.
Background Tasks Kullanımı
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
from fastapi import BackgroundTasks
import aiofiles
import httpx
async def write_log(message: str):
"""Arka planda log yazma"""
async with aiofiles.open("application.log", mode="a") as f:
await f.write(f"{message}\n")
async def send_notification(email: str, message: str):
"""Arka planda email gönderme"""
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
await client.post(
"https://api.sendgrid.com/v3/mail/send",
json={
"to": email,
"subject": "Notification",
"body": message
}
)
@app.post("/send-notification/")
async def create_notification(
email: str,
message: str,
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
# Arka plan görevlerini ekle
background_tasks.add_task(write_log, f"Notification sent to {email}")
background_tasks.add_task(send_notification, email, message)
# Hemen response döndür (görevler arka planda çalışmaya devam eder)
return {"message": "Notification will be sent in background"}
@app.post("/process-file/")
async def process_file(
file_url: str,
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
async def download_and_process():
# Dosyayı indir
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(file_url)
# Dosyayı kaydet
async with aiofiles.open("downloaded_file.dat", mode="wb") as f:
await f.write(response.content)
# İşlemleri yap
await write_log(f"File processed: {file_url}")
# Arka plan görevini ekle
background_tasks.add_task(download_and_process)
return {"message": "File processing started"}
Dependency Injection Sistemi
FastAPI’nin dependency injection sistemi, kod tekrarını azaltır ve test edilebilirliği artırır.
Reusable Dependencies
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
from fastapi import Depends, HTTPException, Header
from typing import Annotated
import jwt
# API Key kontrolü
async def verify_api_key(x_api_key: Annotated[str, Header()]):
if x_api_key != "secret-api-key":
raise HTTPException(status_code=403, detail="Invalid API Key")
return x_api_key
# JWT token kontrolü
async def get_current_user(authorization: Annotated[str, Header()]):
try:
# Bearer token'ı parse et
scheme, token = authorization.split()
if scheme.lower() != "bearer":
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid authentication scheme")
# Token'ı decode et
payload = jwt.decode(token, "SECRET_KEY", algorithms=["HS256"])
username = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid token")
return username
except (ValueError, jwt.JWTError):
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid token")
# Pagination dependency
class PaginationParams:
def __init__(
self,
skip: int = 0,
limit: int = 100,
max_limit: int = 1000
):
if limit > max_limit:
limit = max_limit
self.skip = skip
self.limit = limit
# Protected endpoint örneği
@app.get("/protected")
async def protected_route(
current_user: Annotated[str, Depends(get_current_user)],
api_key: Annotated[str, Depends(verify_api_key)]
):
return {
"message": "Access granted",
"user": current_user
}
# Pagination ile veri çekme
@app.get("/items")
async def list_items(
pagination: Annotated[PaginationParams, Depends()],
db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)
):
# Pagination parametrelerini kullan
result = await db.execute(
select(Item)
.offset(pagination.skip)
.limit(pagination.limit)
)
items = result.scalars().all()
return items
Production Deployment Best Practices
Uvicorn Production Ayarları
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# gunicorn_conf.py
import multiprocessing
# Sunucu ayarları
bind = "0.0.0.0:8000"
workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1
worker_class = "uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker"
# Performans ayarları
keepalive = 120
max_requests = 1000
max_requests_jitter = 50
# Loglama
accesslog = "/var/log/app/access.log"
errorlog = "/var/log/app/error.log"
loglevel = "info"
# Timeout ayarları
timeout = 30
graceful_timeout = 30
Uygulamayı Gunicorn ile çalıştırma:
1
gunicorn main:app -c gunicorn_conf.py
Environment Variables
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
from pydantic_settings import BaseSettings
from functools import lru_cache
class Settings(BaseSettings):
# Uygulama ayarları
app_name: str = "FastAPI App"
debug: bool = False
# Database
database_url: str
# Redis
redis_url: str = "redis://localhost:6379"
# Security
secret_key: str
algorithm: str = "HS256"
access_token_expire_minutes: int = 30
# External APIs
external_api_key: str
external_api_url: str
class Config:
env_file = ".env"
case_sensitive = False
@lru_cache()
def get_settings():
"""Settings singleton - sadece bir kez yükle"""
return Settings()
# Kullanımı
@app.get("/info")
async def info(settings: Settings = Depends(get_settings)):
return {
"app_name": settings.app_name,
"debug": settings.debug
}
Health Check Endpoints
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
from fastapi import status
from sqlalchemy import text
@app.get("/health", status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK)
async def health_check():
"""Basit health check"""
return {"status": "healthy"}
@app.get("/health/detailed", status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK)
async def detailed_health_check(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_db)):
"""Detaylı health check - database bağlantısı kontrol"""
health_status = {
"api": "healthy",
"database": "unknown"
}
try:
# Database bağlantısını test et
await db.execute(text("SELECT 1"))
health_status["database"] = "healthy"
except Exception as e:
health_status["database"] = f"unhealthy: {str(e)}"
# 503 Service Unavailable döndür
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
return JSONResponse(
status_code=status.HTTP_503_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,
content=health_status
)
return health_status
Hata Yönetimi ve Exception Handling
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
from fastapi import HTTPException, Request, status
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from fastapi.exceptions import RequestValidationError
# Custom exception
class ItemNotFoundException(Exception):
def __init__(self, item_id: int):
self.item_id = item_id
# Custom exception handler
@app.exception_handler(ItemNotFoundException)
async def item_not_found_handler(request: Request, exc: ItemNotFoundException):
return JSONResponse(
status_code=status.HTTP_404_NOT_FOUND,
content={
"error": "Item not found",
"item_id": exc.item_id,
"path": request.url.path
}
)
# Validation error handler
@app.exception_handler(RequestValidationError)
async def validation_exception_handler(request: Request, exc: RequestValidationError):
return JSONResponse(
status_code=status.HTTP_422_UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY,
content={
"error": "Validation error",
"details": exc.errors(),
"body": exc.body
}
)
# Global exception handler
@app.exception_handler(Exception)
async def global_exception_handler(request: Request, exc: Exception):
logger.error(f"Global exception: {exc}", exc_info=True)
return JSONResponse(
status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
content={
"error": "Internal server error",
"message": "An unexpected error occurred"
}
)
Sonuç
FastAPI, modern Python web geliştirme için güçlü ve verimli bir framework sunuyor. Asenkron programlama desteği, otomatik dokümantasyon, type safety ve kolay test edilebilirlik özellikleriyle hem küçük projeler hem de büyük ölçekli enterprise uygulamalar için ideal bir seçim.
Bu yazıda öğrendikleriniz:
- FastAPI temel yapısı ve async/await desenleri
- Asenkron veritabanı işlemleri ve connection pooling
- WebSocket ile gerçek zamanlı iletişim
- Middleware ve request/response işleme
- Background tasks ve dependency injection
- Production deployment best practices
Önerilen Kaynaklar
- FastAPI Resmi Dokümantasyonu
- Uvicorn ASGI Server
- Python AsyncIO Dokümantasyonu
- SQLAlchemy Async Extension
- Pydantic V2 Documentation
Bir sonraki yazımızda, Pyrogram kütüphanesi ile Telegram bot geliştirmeyi inceleyeceğiz. Takipte kalın!